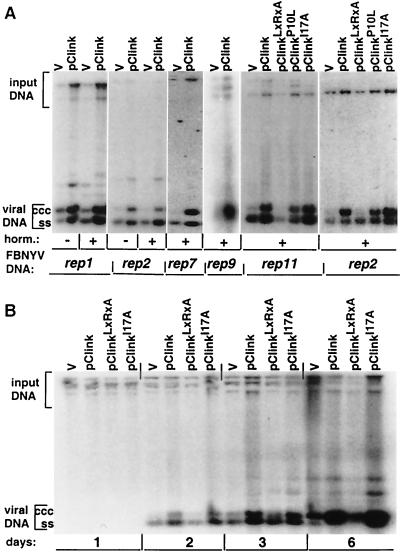
FIG. 4.
Replication enhancement of FBNYV rep DNAs by Clink. Southern hybridization assays of total DNA extracted from leaf discs of N. benthamiana after agroinoculation with pairwise combinations of agrobacteria carrying pBin19 with dimers of a respective rep component (indicated at the bottom [FBNYV DNA]), along with agrobacteria carrying the pBin19 empty vector (v) or wild-type or mutated Clink-encoding FBNYV DNA (indicated at the top) are shown. Leaf disc medium was supplemented (+) or not (−) with plant hormones (horm.). rep-specific probes used for hybridization are shown at the bottom. Replicative forms of viral DNA are marked by ccc (covalently closed circular DNA) and ss (ssDNA). “Input DNA” denotes hybridization with residual pBin19-rep plasmids from agrobacteria used as the inoculum. In each series of experiments, equal amounts of total DNA were loaded, as judged by ethidium bromide staining of the gels (data not shown). The intensities of all DNA bands were quantified upon analysis of the blots with a PhosphorImager (Molecular Dynamics), and stimulation of replication was normalized to the signal produced by the input DNA. (A) DNA was extracted at 3 days after agroinoculation. (B) Leaf discs were agroinoculated with rep2 component and wild-type or mutated Clink-encoding DNA (indicated at the top), and DNA was extracted 1, 2, 3, and 6 days after agroinoculation, as indicated at the bottom.