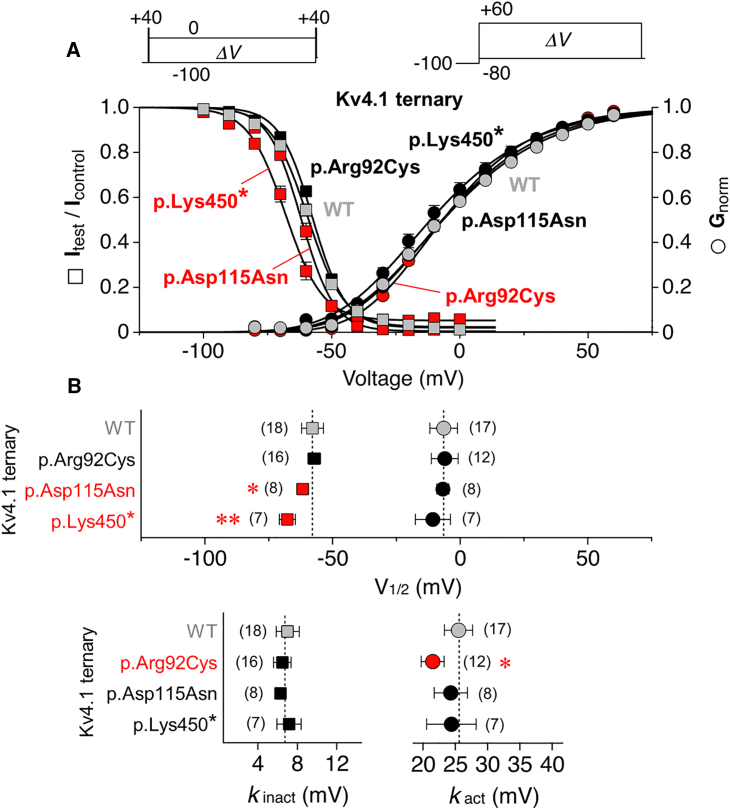
Figure 3.
Voltage dependence of activation and steady-state inactivation
(A) Voltage dependences of peak conductance activation (circles) and steady-state inactivation (squares) are shown for Kv4.1 wild-type (WT), p.Arg92Cys, p.Asp115Asn, and p.Lys450∗ ternary channels. For the study of steady-state inactivation, brief control and test pulses to +40 mV were separated by a 10 s conditioning pulse (ΔV between −100 and 0 mV in 10 mV increments, see inset). Normalized data (Itest/Icontrol) were plotted against the conditioning pulse voltage. For the study of peak conductance activation, test pulses to voltages between −80 and +60 mV (ΔV in 10 mV increments) were applied from −100 mV (see inset). Normalized conductance values were plotted against the test pulse voltage. The data were fitted with appropriate Boltzmann functions.11,36 Gray symbols: Kv4.1 WT; black symbols: data which do not differ from Kv4.1 WT; red symbols: data that differ from Kv4.1 WT (error bars are SEM).
(B) Voltages of half-maximal inactivation (squares) and half-maximal activation (circles) and corresponding slope factors (kinact and kact, respectively); gray symbols and vertical dotted lines: Kv4.1 WT; black symbols: V1/2 and k values of variant ternary channels with no difference compared to Kv4.1 WT; red symbols: V1/2 and k values of variant ternary channels that significantly differ from Kv4.1 WT; number of observations indicated; all statistics based on one way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-hoc testing; significant differences compared to Kv4.1 WT are indicated with ∗p < 0.05 or ∗∗p < 0.0001.