Fig. 2.
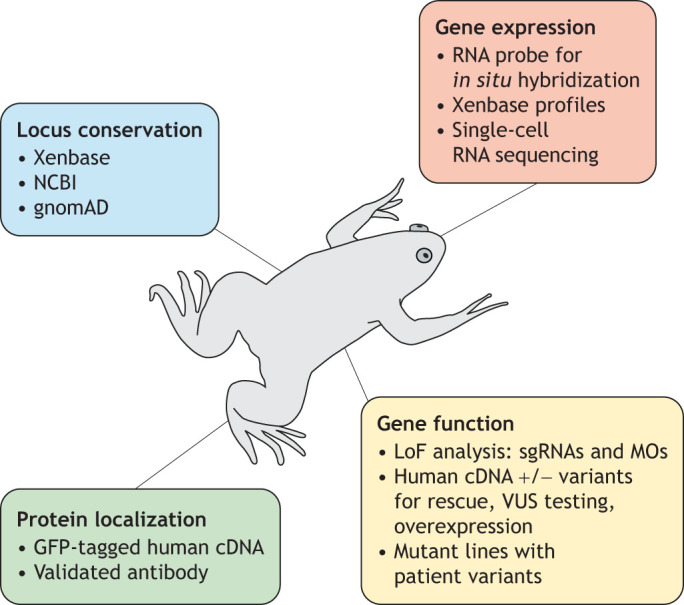
Approaches and tools that facilitate human genetic disease modelling in Xenopus. Once a gene of interest is selected, the locus conservation between X. tropicalis and humans can be explored in Xenbase, NCBI and gnomAD databases. The expression profile of the gene can be queried by using RNA in situ hybridization and on Xenbase. Then the protein can be located in cells and embryos through expression of a tagged human cDNA clone or validated antibody staining. Finally, the function of this gene can be inferred through loss-of-function (LoF) analysis, rescue experiments, overexpression and generating mutant lines with patient-derived variants. This kind of work can quickly point to mechanisms of disease, and tissues and structures for successful studies.
