Fig. 3.
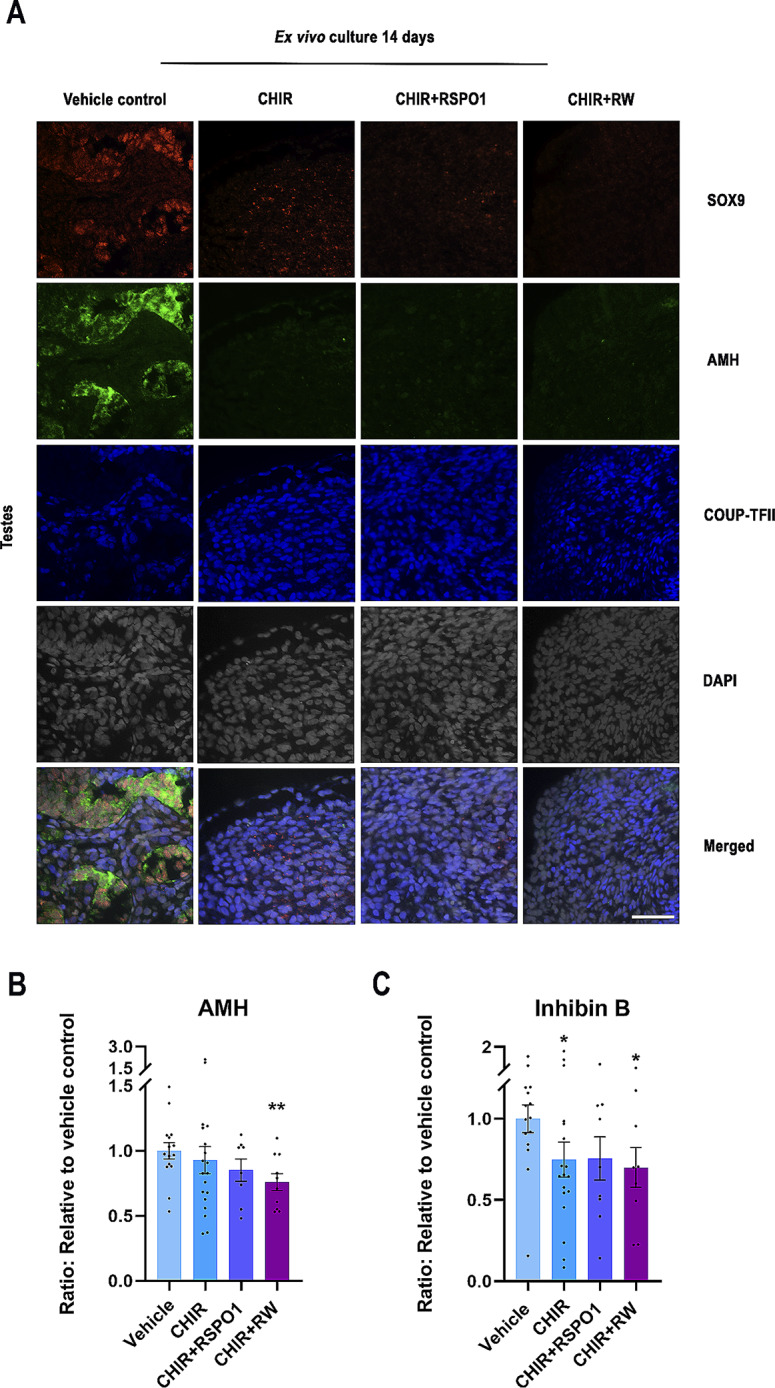
Stimulation of WNT/β-catenin signalling in ex vivo cultures of human fetal testes affected Sertoli cell identity and function. (A) Representative images of triple immunofluorescence staining of SOX9 (Sertoli cell marker, red), AMH (Sertoli cell marker, green), COUPTF-II (Interstitial cell marker, blue) and DAPI (grey) in ex vivo cultured fetal testes treated with CHIR (3 µM), CHIR + RSPO1: CHIR (3 µM) + RSPO1 (100 ng/ml) or CHIR + RW: CHIR (3 µM) + RSPO1 (100 ng/ml) + WNT4 (100 ng/ml). Age of fetal samples shown (at start of experiment): Vehicle control 9 + 0 PCW; CHIR 9 + 0 PCW; CHIR + RSPO1 9 + 4 PCW; CHIR + RW 9 + 0 PCW. Scale bar corresponds to 50 μm. (B) Secretion of AMH measured in media from ex vivo cultured fetal testes treated with CHIR (n = 19), CHIR + RSPO1 (n = 9) or CHIR + RW (n = 10). (C) Inhibin B measured in media from ex vivo cultured fetal testes treated with CHIR (n = 18), CHIR + RSPO1 (n = 9) or CHIR + RW (n = 9). Results are shown as fold change compared to internal vehicle control with data presented as mean ± SEM with individual datapoints included. Asterisk indicates statistical significance compared to vehicle control with * P < 0.05 and ** P < 0.01
