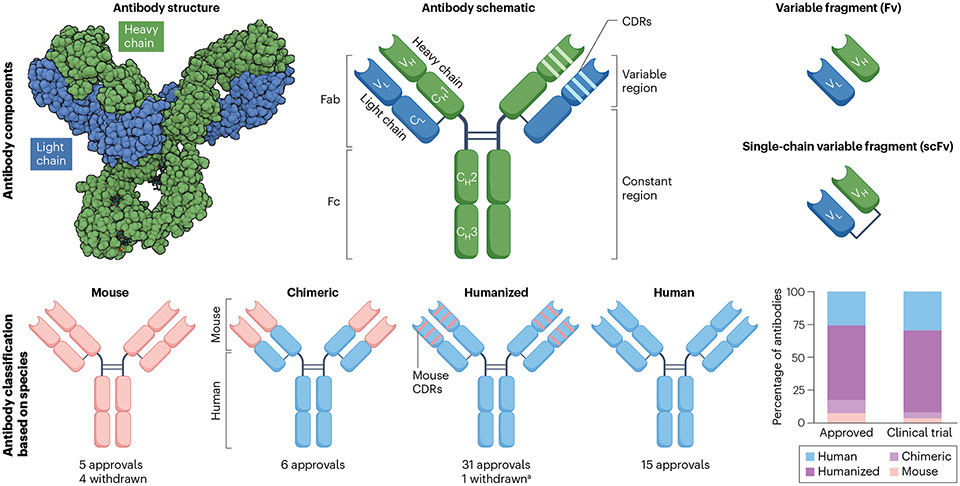
Fig. 1 ∣. Antibody components.
a, Antibodies consist of two identical light chains and heavy chains that are held together by disulfide bonds and resemble a Y-shaped structure. Each light and heavy chain contains a variable (VL and VH) domain responsible for antigen binding and constant (CL and CH) domains that determine the half-life and effector function of the antibody. Enzymatic processing can break up antibodies into two fragments named fragment antigen binding (Fab) and fragment crystallizable (Fc). The light and heavy chain variable regions together make up the fragment variable (Fv), the smallest fragment that retains antigen-binding capacity. Manufactured Fv fragments are joined together by a flexible peptide linker to form a single chain named single-chain variable fragment (scFv). Antibodies are grouped as mouse, chimeric, humanized and human based on the amount of peptide sequence derived from each species. aBelantamab mafodotin was withdrawn but may gain re-approval based on ongoing trials. Teclistamab (a combination of a humanized and a human antibody) is considered as a humanized antibody for this figure. CDRs, complementarity-determining regions.