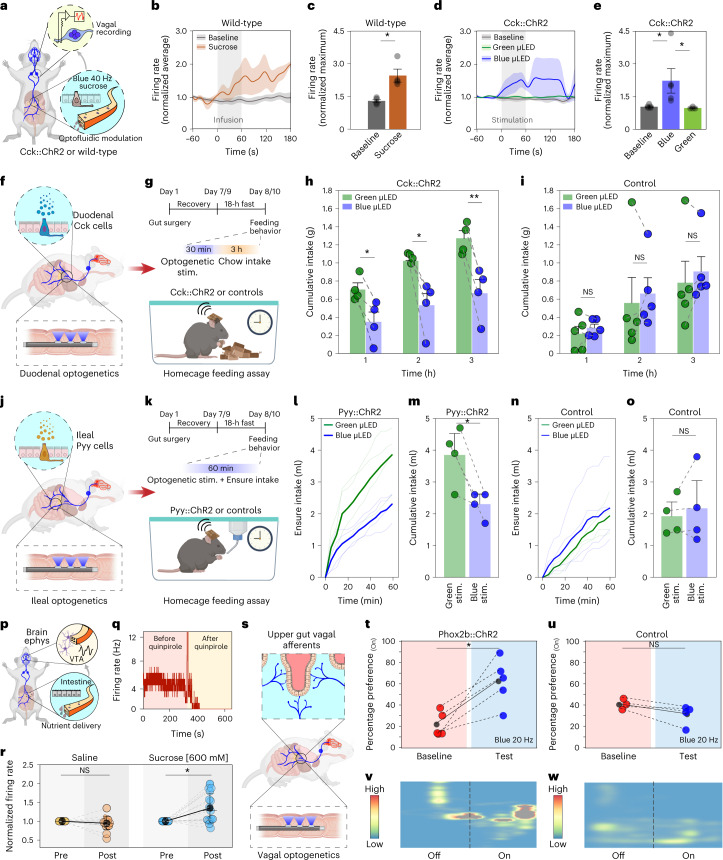
Fig. 6. Multimodal interrogation of gut neural circuits and wireless programmable optogenetics during behavior.
a, Vagal electrophysiology during intestinal optofluidic modulation. b, Duodenal sucrose (300 mM) increases vagal firing rate. c, Quantification of peak responses (n = 4; *P = 0.0304 by Kruskal–Wallis test with nonparametric comparisons using Wilcoxon method). d, Optogenetic stimulation of Cck+ cells increases vagal firing rate. e, Quantification of peak responses; *P < 0.0367 by Kruskal–Wallis test with nonparametric comparisons using Wilcoxon method, baseline (n = 5) versus blue µLED (n = 5): P = 0.0367; baseline versus green µLED (n = 4): P = 0.1113; blue µLED versus green µLED: P = 0.0200. f,g, Schematic of wireless intraduodenal optogenetic control of Cck+ cells (f) while evaluating feeding behavior (g). h,i, Chow intake in (h) Cck::ChR2 mice (n = 4, significant effect of time (P = 0.0003), stimulation (P < 0.0001) and time × stimulation interaction (P = 0.0086); post hoc two-sided paired t-tests: 1 h, P = 0.0161; 2 h, P = 0.0376; 3 h, P = 0.0044) and for (i) control mice lacking ChR2 (n = 4, significant effect of time (P = 0.0020), but not stimulation (P = 0.4975) or time × stimulation interaction (P = 0.8906)). j,k, Illustration of ileal optogenetic control of Pyy+ cells (j) while evaluating food intake (k). l, Ensure intake for Pyy::ChR2 mice during wireless optical stimulation (n = 4, significant effect of time (P < 0.0001), stimulation (P < 0.0001) and time × stimulation interaction (P < 0.0001)). m, Cumulative intake of l (two-sided paired t-test, P = 0.0381). n, Ensure intake for control mice (n = 4 mice, significant effect of time (P < 0.0001) and stimulation (P = 0.0160), but no significant time × stimulation interaction (P = 0.5796)). o, Cumulative intake for n (two-sided paired t-test, P = 0.4639). p, Schematic of brain VTA electrophysiology during duodenal microfluidic infusion. q, Firing rate of a putative DA neuron is sensitive to quinpirole. r, Intraduodenal sucrose increases firing rate of putative DA neurons compared with saline (saline: n = 20; sucrose: n = 18 neurons; two-sided Wilcoxon signed-rank test, P = 0.8595, P = 6.71387 × 10−4, respectively). s, Schematic of duodenal optogenetic stimulation in Phox2b::ChR2 mice. t,u, Percentage preference at baseline and on test day for Phox2b::ChR2 (t) and control mice lacking ChR2 (u) (two-sided paired t-test, Phox2b::ChR2: P = 0.014, t = 4.19, d.f. = 4; control mice: P = 0.110, t = –2.25, d.f. = 3). v,w, Representative heat-maps of animal position corresponding to t (v) and u (w). All data are represented as mean ± s.e.m, except in r which shows mean ± s.d. Ephys, electrophysiology.