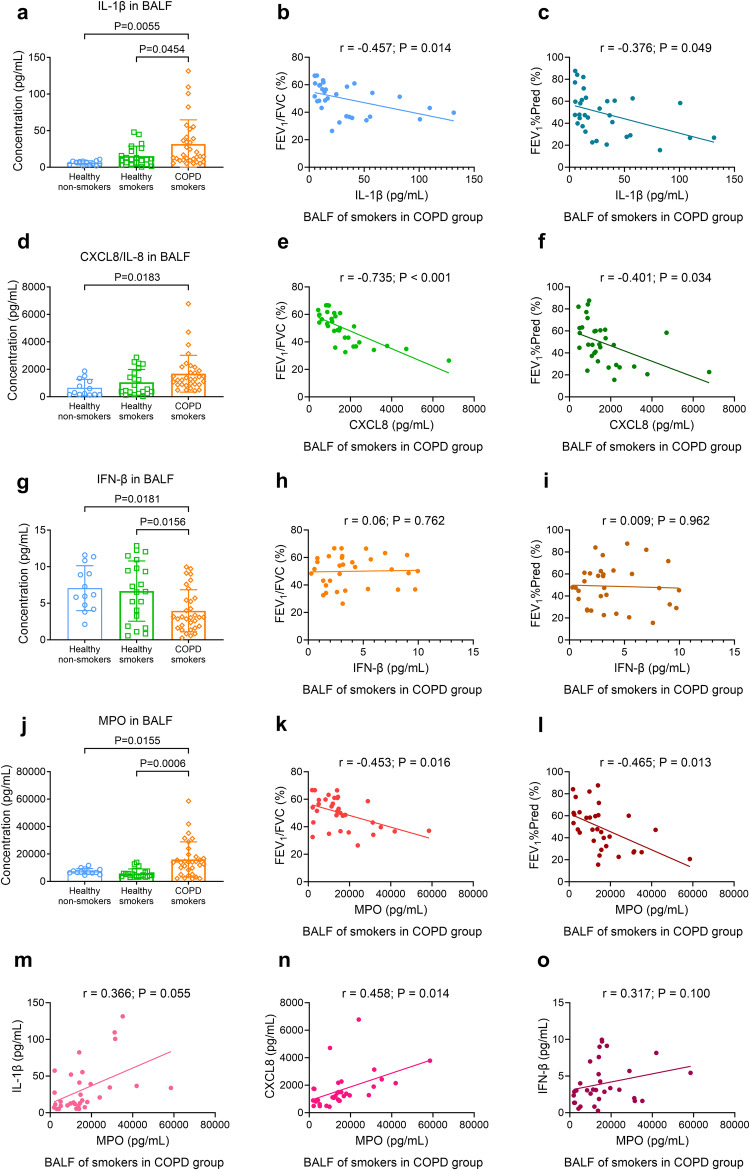
Fig. 8.
The level of myeloperoxidase (MPO) is correlated with the level of interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and level C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 8 (CXCL8), but not correlated with the level of interferons-β (IFN-β) in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) of smokers in the group of patients with COPD, after controlling for their age, sex, body mass index (BMI) and smoking history. Statistical analysis: n = 13 non-smokers and 21 smokers in group of healthy participants, n = 32 smokers in group of patients with COPD in (a, d, g, j), n = 32 in (b, c, e, f, h, i, k–o), data were presented as the mean ± standard deviation; Differences in (a, d, g, j) are assessed by one-way analysis of variance, followed Tukey’s honest significant test; In (b, c, e, f, h, i, k, l, m–o), Pearson’s partial correlation test are performed by controlling for age, sex, BMI and smoking history of smokers in the group of patients with COPD, followed by the multiple linear regression analysis; P < 0.05 represents a significant difference, the scattered samples and the p values are displayed in figures. a IL-1β level is significantly increased in the BALF of smokers in the group of patients with COPD, compared with that of non-smokers and smokers in the healthy group, and negatively correlated with b ratio of FEV1 to forced vital capacity (FEV1/FVC), and c ratio of forced expiratory volume at 1 s (FEV1) to predicted FEV1 (FEV1%Pred, supplementary Method 1, 2, 3, 26), respectively. d CXCL8 level is significantly increased in the BALF of smokers in the group of patients with COPD, compared with that of non-smokers in the healthy group, and negatively correlated with e FEV1/FVC and f FEV1%Pred, respectively. g IFN-β level is significantly decreased in the BALF of smokers in the group of patients with COPD, compared with that of non-smokers and smokers in the healthy group; There is no correlation between IFN-β level and h FEV1/FVC, or IFN-β level and i FEV1%Pred. j MPO level is significantly increased in the BALF of smokers in the group of patients with COPD, compared with that of non-smokers and smokers in the healthy group, and negatively correlated with k FEV1/FVC and l FEV1%Pred, respectively. In the BALF of COPD smokers, MPO level is correlated with the level of n CXCL8, but not the level of m IL-1β or o IFN-β