FIGURE 3.
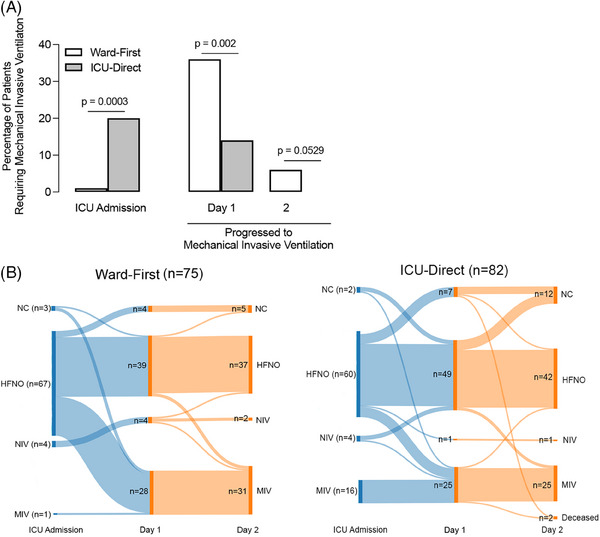
Ward‐first patients required more rapid escalation to mechanical ventilation within 1 day of intensive care unit (ICU) admission compared to ICU‐direct patients. (A) At time of ICU admission, a greater percentage of ICU‐direct patients (n = 16 out of 82, 20%) required mechanical invasive ventilation (MIV) as compared to ward‐first patients (n = 1 out of 75, 1%). However, more ward‐first patients (n = 27 out of 74, 36%) who were admitted to the ICU on high flow nasal oxygen (HFNO) or non‐invasive ventilation (NIV, inclusive of continuous positive airway pressure and bilevel positive airway pressure) progressed to requiring MIV within 1 day compared to ICU‐direct patients (n = 9 out of 66 patients, 14%). More ward‐first patients progressed to MIV on day 2 of ICU admission compared to ICU‐direct patients; however, this was not statistically significant. (B) Sankey diagrams illustrate progression of respiratory support needs for ward‐first (left) and ICU‐direct (right) patients at ICU admission and days 1 and 2 of ICU stay. NC, nasal cannula.
