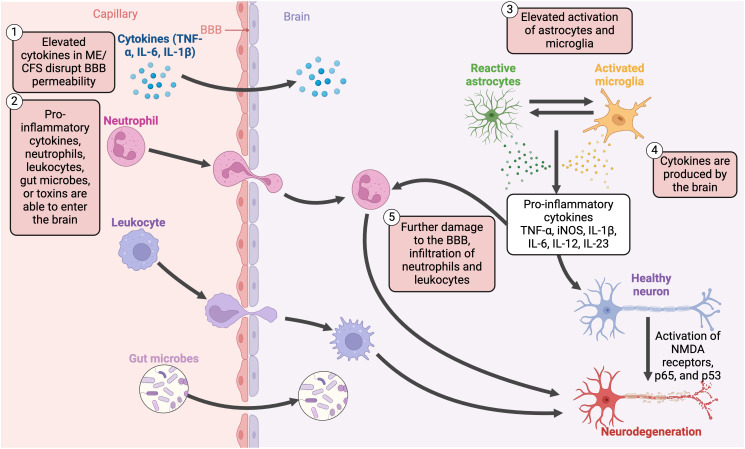
Figure 10.
Disruption of the blood-brain barrier, the translocation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and chronic activation of various non-neuronal cells contribute to neuroinflammatory mechanisms in ME/CFS (45, 47, 52, 201, 251, 354, 355). Created with Biorender.com. BBB, blood-brain barrier; IL, interleukin; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; ME/CFS, Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome; NMDA, N-methyl-D-aspartate; TNF-α, tumour necrosis factor alpha.