Fig. 4.
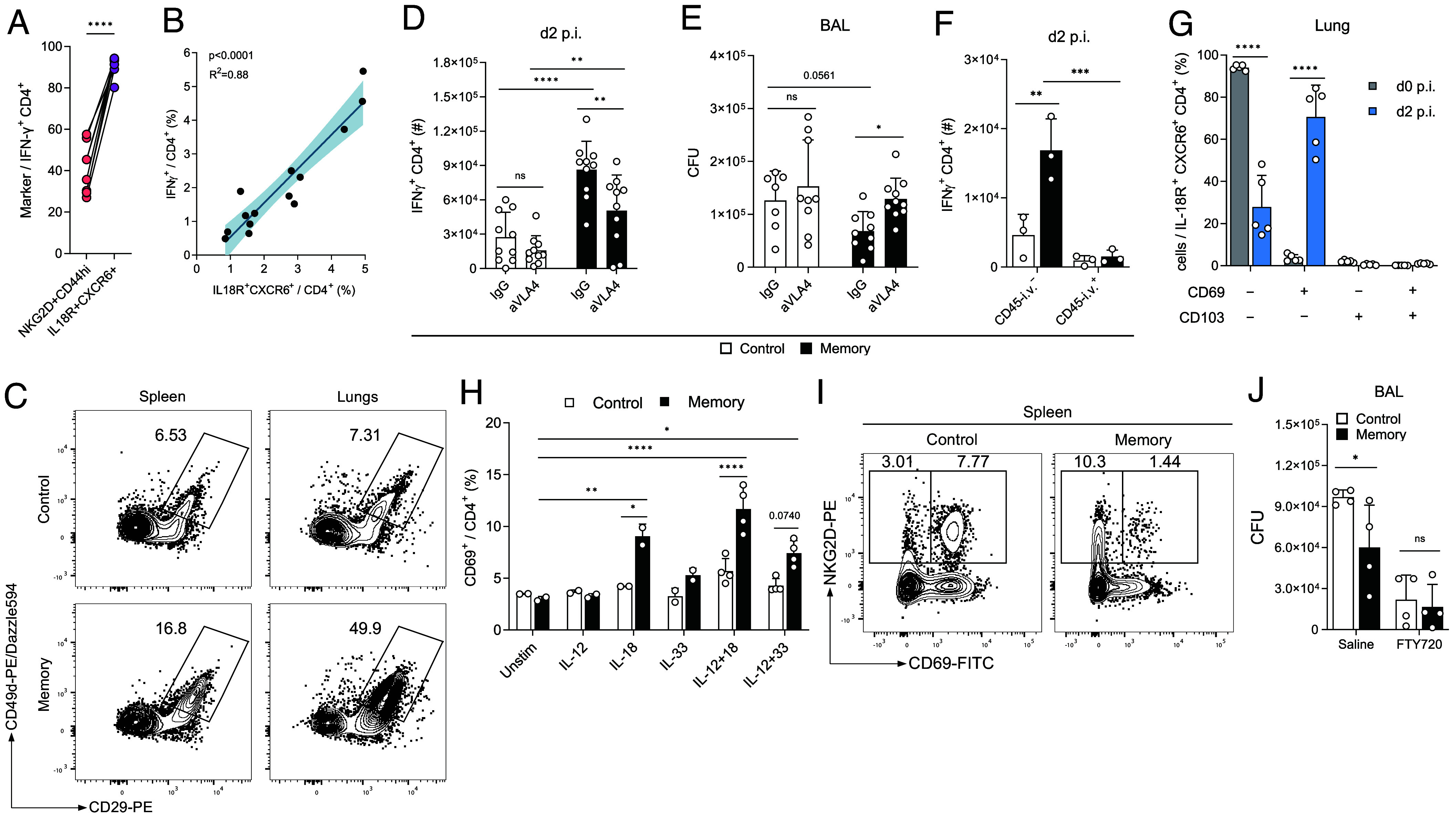
CD4+ TIA cells have enhanced migratory capabilities. (A) Ex vivo expression of indicated markers in lung CD4+ T cells upon Lpn infection of LCMV memory mice (n = 10). (B) Linear regression of splenic control and memory CD4+ T cells stained ex vivo (x axis) and IFN-g production upon overnight IL-12+IL-18 stimulation (y axis). 95% CI is indicated (n = 14). (C) Representative FACS plots of integrin expression of Lpn challenged control vs. LCMV memory CD4+ T cells 2 dpi. (D and E) IFN-g response in lung CD4+ T cells (D) and Lpn titers (E) 2 dpi in mice treated with a-VLA4 blocking antibody or IgG control during Lpn challenge (n = 10). (F) Mice injected with aCD45 antibody i.v. prior to sacrifice (n = 3). (G) Expression of indicated markers among TIA cells (n = 5). (H) CD69 expression in isolated splenic CD4+ T cells incubated with indicated cytokines overnight was determined by FACS (n = 2 to 4). (I) Representative FACS plot of splenic CD44+CD4+ T cells in control vs. LCMV memory mice pre-Lpn infection. (J) Lpn titers 3 dpi in mice treated with FTY720 or saline i.p. (n = 4). Mean ± SD, paired t test (A) and ordinary two-way ANOVA (Šídák; D–H and J).
