Abstract
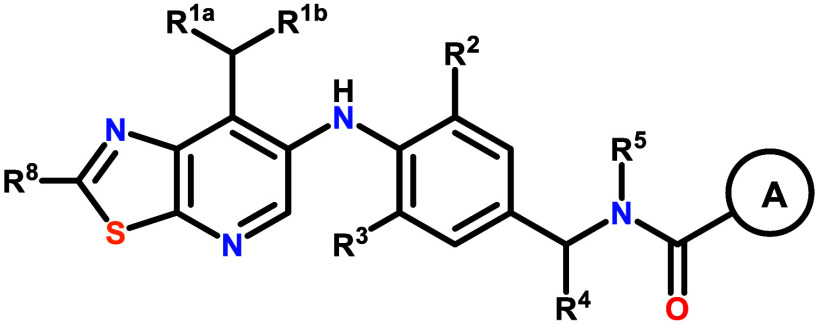
The invention in this patent application relates to thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridine derivatives represented generally by formula 1. These compounds are inhibitors of the activity of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1 (MALT-1) protease and may potentially be useful in the treatment of some forms of cancer, particularly ABC-DLBCL.
Important Compound Classes
Formula 1:
Title
Thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridine MALT-1 Inhibitors
Patent Publication Number
WO 2023/192913 A1
https://patentimages.storage.googleapis.com/62/81/b1/e35cd9defd0d77/WO2023192913A1.pdf
Publication Date
October 5, 2023
Priority Application
US 63/362,302
Priority Date
March 31, 2022
Inventors
Cohen, D. T.; Gong, J.; Jain, T.; Kumar, P.; Liu, D.; Mastracchio, A.; Mills, M.; Phillips, A. W.; Pratt, J. K.; Punna, S.; Stockwell, J. A.; Wang, L.; Yu, Y.
Assignee Company
AbbVie Inc., 1 N Waukegan Road, AP3402 V377, North Chicago, IL 60064, USA
Disease Area
Activated B cell-like subtype diffuse large B cell lymphoma (ABC-DLBCL) and possibly other forms of cancer
Biological Target
The human paracaspase, mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1 (MALT-1)
Summary
Paracaspases are cysteine proteases that are related to the caspase protease enzyme family. The members of this family play essential roles in programmed cell death in different species, including humans. The only known human paracaspase is mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1 (MALT-1).
The B and T cells of the adaptive immune system utilize the pleiotropic nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) signaling pathway to transduce extracellular signals from cognate antigen receptors to increase survival and proliferation. This signal transduction leads to a rapid nuclear localization of NF-κB and activation of target genes, including proinflammatory cytokines and negative regulators of apoptosis.
The stimulation of B cell receptor and T cell receptor results in the formation of a signaling complex composed of the caspase recruitment domain family member 11 (CARD11), the B cell CLL/lymphoma 10 (BCL10), and the paracaspase MALT-1. This signaling complex is known by its abbreviated name, CARD11-BCL10-MALT-1 complex, or simply CBM complex. The CBM complex is a key downstream signaling hub of the NF-κB pathway. It recruits multiple signaling proteins, which is a function that sets canonical NF-κB activation in motion.
The NF-κB activation by the CBM complex reveals important roles of MALT-1 as a necessary scaffold protein in assembling the CBM complex as well as an essential key activator of NF-κB within this complex. However, MALT-1 roles do not stop there—it also acts as a protease to cleave the negative regulators of the NF-κB pathway for signal reinforcement.
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is a form of B-cells cancer, which is categorized into two distinct molecular subtypes: activated B-cell-like (ABC) and germinal center B-cell-like (GCB). Studies have linked aberrant activation of NF-κB signaling with DLBCL. Gain-of-function mutations of the B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling pathway have been detected frequently in DLBCL. These mutations can initiate constitutive activation of NF-κB, which is required for tumor cell survival.
One kind of DLBCL tumor is the activated B-cell-like subtype diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (ABC-DLBCL) that is characterized by chronically active BCR signaling pathway, which stimulates NF-κB.
Deregulated MALT-1 activity has been implicated in various human diseases. For example, the function of MALT-1 as an activator of the NF-κB pathway plays an essential role in promoting DLBCL cancers such as ABC-DLBCL. Therefore, the inhibition of MALT-1 protease has emerged as a therapeutic target to provide a viable treatment for these diseases. However, there remains a specific need for novel and effective inhibitors of MALT-1 activity with improved potency and pharmaceutical properties as potential therapy for the treatment of ABC-DLBCL and similar diseases.
The disclosed compounds of formula 1 in this patent application have displayed activities as inhibitors of MALT-1 protease and may potentially provide a treatment for ABC-DLBCL or related cancers.
Key Structures
The inventors described the structures
and procedures for the synthesis of 39 examples of compounds of formula 1. The following structures are representative examples: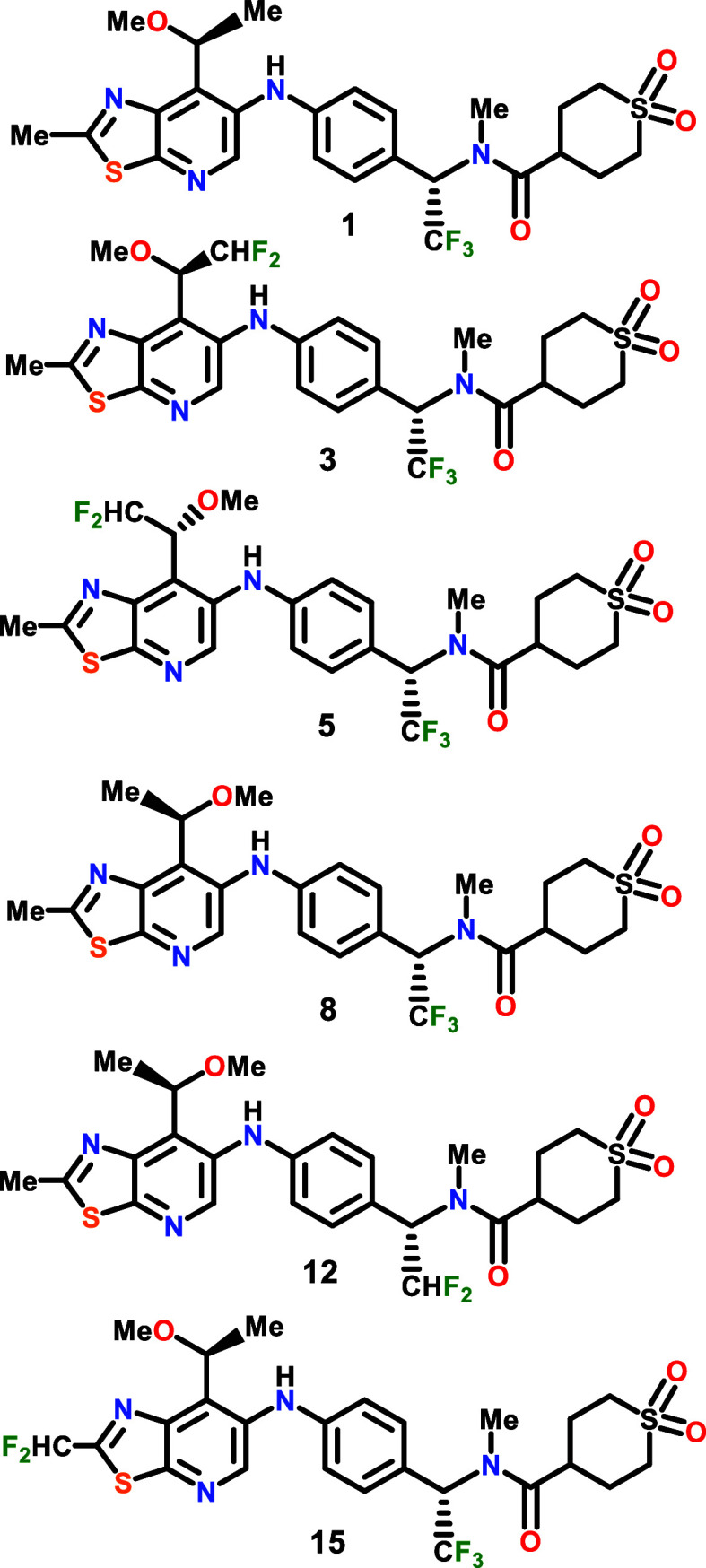

Biological Assays
The inventors used the following assays to test the compounds of formula 1:
-
1.
MALT-1 Biochemical Assay
-
2.
MALT-1 Cell IL-6 AlphaLISA Assay
-
3.
Cardiovascular Assay
-
4.
CYP3A4 Induction Assay
Biological Data
The data obtained from testing the
representative examples by assays 1 and 2 above are summarized in
the following table.
Recent Review Articles
The author declares no competing financial interest.
References
- Plotnik J. P.; Richardson A. E.; Yang H.; Rojas E.; Bontcheva V.; Dowell C.; Parsons S.; Wilson A.; Ravanmehr V.; Will C.; et al. Inhibition of MALT1 and BCL2 induces synergistic antitumor activity in models of B cell lymphoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2024, 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-23-0518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimberger N.; Ober F.; Avar G.; Grau M.; Xu W.; Lenz G.; Menden M. P.; Krappmann D. Oncogene-induced MALT1 protease activity drives posttranscriptional gene expression in malignant lymphomas. Blood 2023, 142 (23), 1985–2001. 10.1182/blood.2023021299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhelst S. H. L.; Prothiwa M. Chemical Probes for Profiling of MALT1 Protease Activity. ChemBioChem 2023, 24 (21), e202300444. 10.1002/cbic.202300444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill T. J.; Tofaute M. J.; Krappmann D. Function and targeting of MALT1 paracaspase in cancer. Cancer Treatment Reviews 2023, 117, 102568. 10.1016/j.ctrv.2023.102568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y.-Y.; Peng J.; Luo X.-J. Post-translational modification of MALT1 and its role in B cell- and T cell-related diseases. Biochemical Pharmacology 2022, 198, 114977. 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.114977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]