Fig. 4. Competitive ELISA measuring binding of ACE2 receptor to DCFHP samples in solution and adsorbed to Alhydrogel adjuvant.
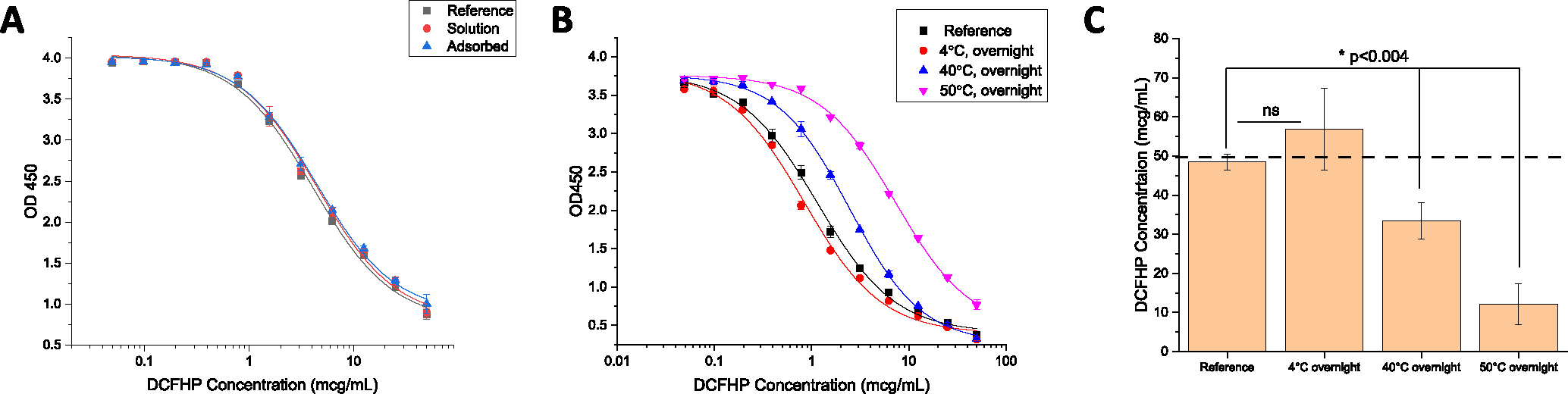
(A) Representative ELISA curves comparing ACE2 binding of DCFHP antigen in solution and adsorbed to Alhydrogel (AH). (B) Representative ELISA curves of AH-adsorbed DCFHP incubated at 4°, 40°, and 50 °C overnight and compared to a DCFHP reference sample that was adsorbed to AH on the same day of the assay. (C) Native antigen concentration (50 mcg/mL target) of thermally-stressed AH-adsorbed DCFHP samples as determined from the logistic ELISA curve fits (see Supplemental methods section) (panel B) versus the DCFHP reference sample. Data are the mean of two independent experiments, which contained two replicates (n=4) with the error bars representing the standard deviation. The dashed line represents the target concentration of 50 mcg/mL. DCFHP samples were prepared at 50 mcg/mL in 20 mM Tris, 150 mM NaCl, 5% Sucrose, pH 7.5 buffer, with and without being adsorbed to 1.5 mg/mL AH. (*) and (ns) indicate a statistically significant (p <0.004) vs. not significant difference, respectively, between the freshly adsorbed reference DCFHP sample vs. various thermally-treated samples by a two-tailed t-test.
