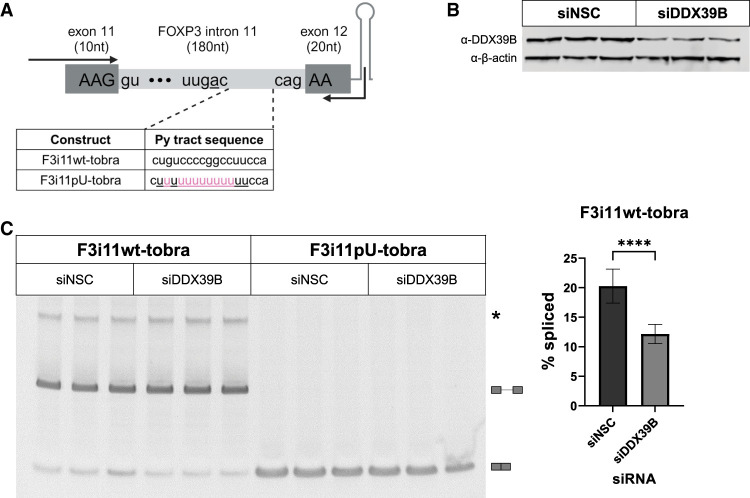
FIGURE 2.
Splicing of a FOXP3 intron 11 tobramycin aptamer construct is sensitive to DDX39B. (A) Schematic diagram of FOXP3 intron 11-tobramycin constructs, which encompass the last 10 nt of exon 11, intron 11 wt (F3i11wt-tobra) or U-rich mutant (F3i11pU-tobra), first 20 nt of exon 12, followed by the tobramycin aptamer sequence. Highlighted in pink are nucleotide changes made to F3i11wt-tobra to create a stretch of 13 consecutive Us in py tract of F3i11pU-tobra. Black arrows represent the location of primers used for end point PCR to quantify splicing efficiency (created with BioRender). (B) Representative western blot of siRNA-mediated depletion of DDX39B (siDDX39B) compared to siNSC. β-Actin was used as a loading control. (C) End point PCR analysis of FOXP3 intron splicing from the F3i11wt-tobra and F3i11pU-tobra constructs in HeLa cells treated with siNSC or siDDX39B. Quantification of % splicing of F3i11wt-tobra (calculated as (spliced/[spliced + unspliced]) × 100) represents the average ± SD of nine biological replicates from three independent experiments; (****) P < 0.0001, Student's t-test.