FIGURE 6.
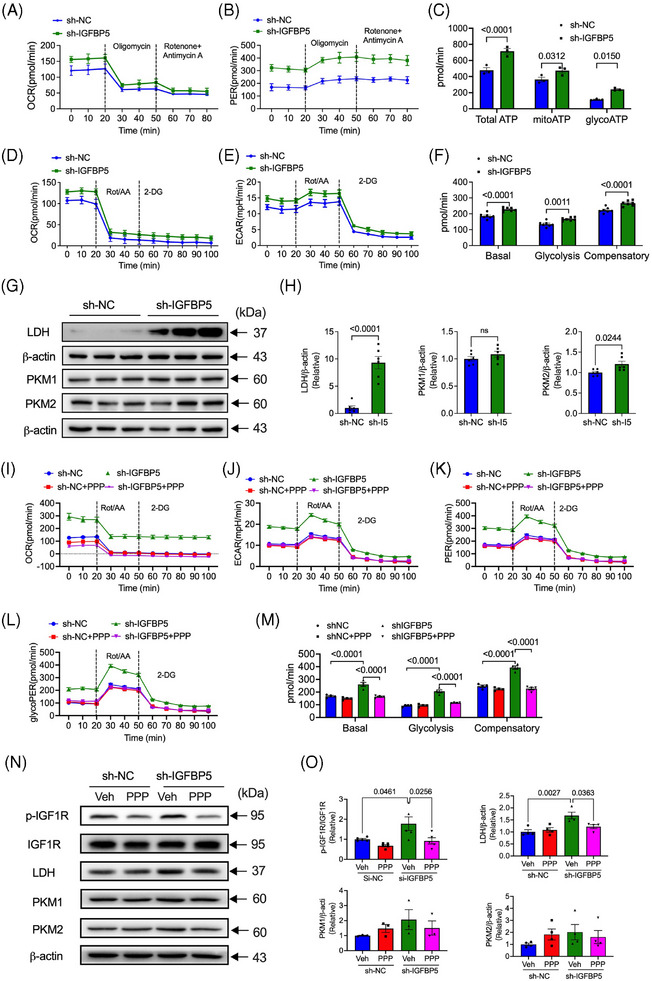
Insulin‐like growth factor‐binding protein 5 (IGFBP5) deficiency promotes glycolysis through IGF1R. (A) OCR and (B) ECAR profiles in sh‐NC‐ and sh‐IGFBP5‐infected human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) (n = 8 in each group). (C) Quantification of ATP production in sh‐NC‐ and sh‐IGFBP5‐infected HUVECs. (D) OCR and (E) ECAR profiles showing the glycolytic function in sh‐NC‐ and sh‐IGFBP5‐infected HUVECs (n = 8 in each group). (F) Quantification of glycolytic function parameters in sh‐NC‐ and sh‐IGFBP5‐infected HUVECs (n = 8 in each group). (G) Western blotting images and (H) quantification of the expression of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), PKM1 and PKM2 in sh‐NC‐ and sh‐IGFBP5‐infected HUVECs. (I) OCR, (J) ECAR, (K) proton efflux rate (PER) and (L) glycoPER profiles showing glycolytic function in sh‐NC‐ and sh‐IGFBP5‐infected HUVECs in the presence or absence of IGF1R inhibitor picropodophyllin (PPP) (n = 6 in each group). (M) Quantification of glycolytic function parameters in sh‐NC‐ and sh‐IGFBP5‐infected HUVECs in the presence or absence of PPP (n = 8 in each group). (N) Western blot images and (O) quantification of the expression of LDH, PKM1 and PKM2 in sh‐NC‐ and sh‐IGFBP5‐infected HUVECs in the presence or absence of IGF1R inhibitor PPP (n = 6 in each group).
