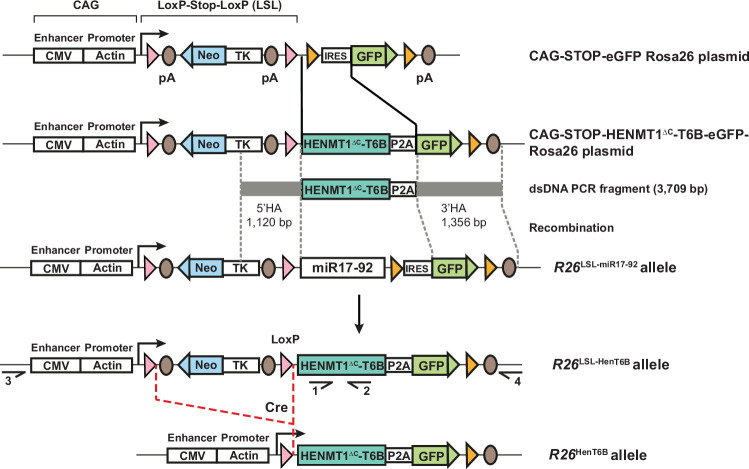
Figure EV2. Generation of the R26LSL-HenT6B allele.
The HENMT1∆C-T6B cDNA was cloned in the CAG-STOP-eGFP-Rosa26 TV plasmid by replacing the IRES sequence with the HENMT1∆C-T6B cDNA fused in frame via a P2A peptide to the eGFP coding sequence to generate the CAG-STOP-HENMT1∆C-T6B-eGFP-Rosa26 plasmid. A 3,709-bp PCR fragment containing a 1120-bp 5´ homology arm (HA) and a 1356-bp 3´ HA was used as double-stranded DNA repair template together with two sgRNAs to replace the miR17-92-IRES DNA sequences of the R26LSL-miR17-92 allele26 by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing in mouse 2-cell embryos, resulting in the R26LSL-HenT6B allele. Cre-mediated deletion of the loxP-Stop-loxP (LSL) cassette leads to the expression of the HENMT1∆C-T6B-P2A-eGFP gene from the ubiquitously transcribed CAG promoter of the R26HenT6B allele. LoxP and frt sites are indicated by red and yellow arrowheads, respectively. The herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase (TK) promoter drives expression of the neomycin (Neo) resistance gene. Arrows indicate primers 1 and 2 used for genotyping of the R26LSL-HenT6B allele and primers 3 and 4 used for genotyping of the wild-type R26 allele (see Methods). pA, polyadenylation sequence.