FIGURE 1.
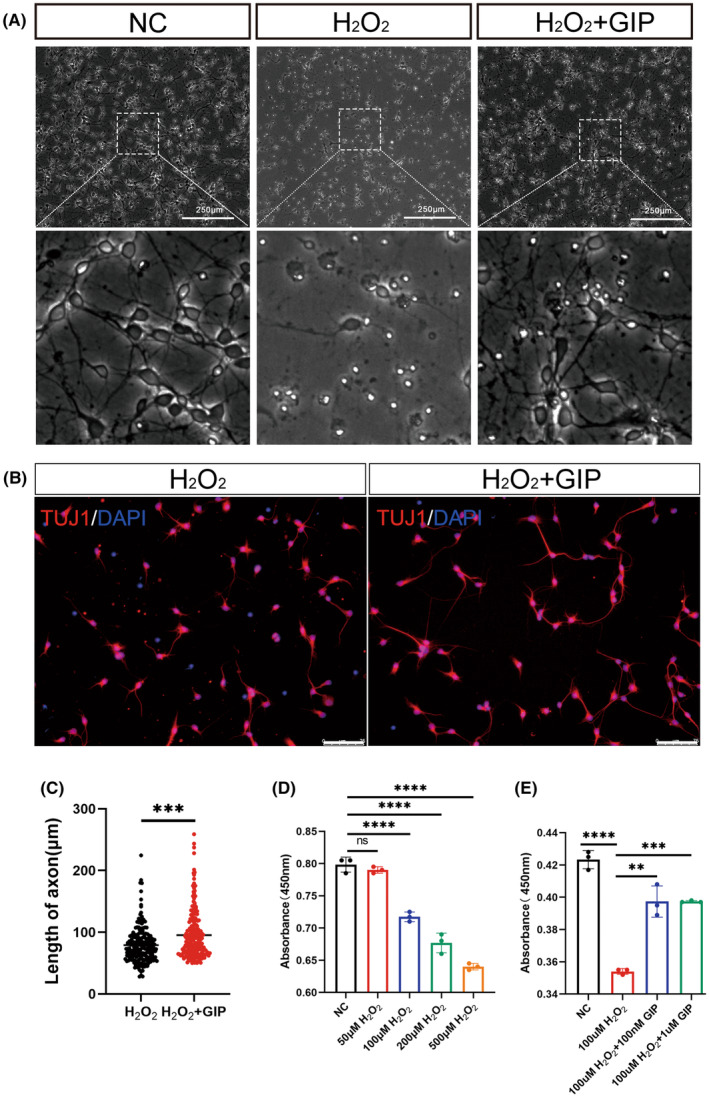
GIP restored the cell viability of primary cultured E18 cortical neurons after oxidative damage. (A) Representative images of neurons after 3 h of H2O2 injury and 24 h of GIP treatment. The enlarged views of dotted boxes were shown in the down panel. Scale Bar = 250 μm. (B) Representative images of neurons stained with anti‐TUJ1 (red), DAPI (blue) after 3 h of H2O2 injury and 24 h of GIP treatment. Scale Bar = 75 μm. (C) GIP increased the length of the axon. The data were shown as mean ± SE, and were analyzed by Student's t‐test, n = 200–220 neurons for each group per test, N = 3 (cells were from rats interpedently). ***p < 0.001. (D) Cell viability was evaluated by CCK8 assay after treatment with different concentrations of H2O2. The data were shown as mean ± SE, and were analyzed by one‐way ANOVA, n = 3, ns represents no statistical difference, ****p < 0.0001. (E) GIP attenuates the detrimental effect of H2O2 on cultured neurons. Neurons were treated with 100 μM H2O2 for 3 h and treated with 100 nM or 1 μM GIP for 24 h. The data were shown as mean ± SE, and were analyzed by one‐way ANOVA, n = 3. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
