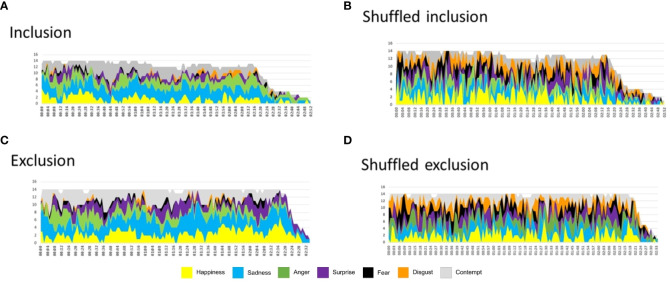
Figure 4.
(A). Inclusion Patterns of the primary emotions 1) Happiness, 2) Sadness, 3) Anger, 4) Surprise, 5) Fear, 6) Disgust, and 7) Contempt. (B). Shuffled Inclusion shows that the patterns in A are lost. 1)Happiness vs. Shuffled Happiness (t = 2.41, p< 0.01); 2) Sadness vs. Shuffled Sadness (t = 10.55, p< 2.27611E−20); 3) Anger vs. Shuffled Anger (t = 5.54, p< 1.07248E−07); 4) Surprise vs. Shuffled Surprise (t = 4.41, p< 1.78844E − 05); 5) Fear vs. Shuffled Fear (t = 9.66, p< 6.45638E − 18); 6) Disgust vs. Shuffled Disgust (t = 9.89, p< 1.55306E − 18); and 7) Contempt vs. Shuffled Contempt (t = 5.79, p< 3.16769E − 08). More details in the text. (C). same as A for exclusion patterns (D). Shuffled Exclusion shows that the patterns in A are lost. 1)Happiness vs. Shuffled Happiness (t = 3.76, p< 0.0002), 2) Sadness vs. Shuffled Sadness (t = 9.34, p< 1.04266E − 16), 3) Anger vs. Shuffled Anger (t = 1.5912, p< 0.11), 4) Surprise vs. Shuffled Surprise (t = 1.07, p< 0.28), 5) Fear vs. Shuffled Fear (t = 9.38, p< 8.28122E − 17), 6) Disgust vs. Shuffled Disgust (t = 10.91, p< 7.29614E − 21), and 7) Contempt vs. Shuffled Contempt (t = 4.06, p< 7.67073E − 05). More details in the text.