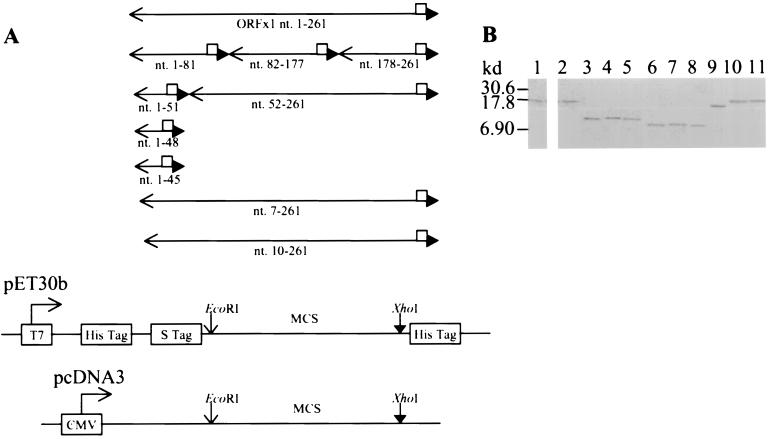
FIG. 1.
Construction of eukaryotic and prokaryotic vectors expressing full-length and mutant p10. (A) PCR performed with specific primer pairs (available upon request) amplified the DNA fragments encoding the full-length p10 (nt. 1-261) consisting of 87 residues, the N-terminal 27 residues (nt. 1-81), the 32-residue peptide 28-59 (nt. 82-177), the C-terminal 28-residue peptide 60-87 (nt. 178-261), the N-terminal 17 residues (nt. 1-51), the N-terminal 16 residues (nt. 1-48), the N-terminal 15 residues (nt. 1-45), and the N-terminal truncated p10Δ2 (nt. 7-261), p10Δ3 (nt. 10-261), and p10Δ17 (nt. 52-261). The cDNA of ORFx1 previously cloned into the pGEX4T-3 vector (Pharmacia) to yield the pGEX-ORFx1 plasmid (5) was used as the template in the PCR. One primer contained an EcoRI site plus 3 bases at the 5′ end, while the second primer had the DNA sequence encoding the FLAG epitope, followed by an XhoI site, plus 3 bases at the 5′ end. The amplified DNA fragments were digested by EcoRI and XhoI and cloned into the pET-30b vector (Novagen), in frame and downstream of the sequence encoding for the His and S tags, to yield the pET-ORFx1-FLAG, pET1-81-FLAG, pET82-177-FLAG, pET178-261-FLAG, pET1-51-FLAG, pET1-48-FLAG, pET1-45-FLAG, pET7-261-FLAG, pET10-261-FLAG, and pET52-261-FLAG plasmids, respectively. Cloning of the ORFx1 DNA fragments containing nt 1 to 51 and nt 52 to 261 into the pcDNA3 eukaryotic expression vector yielded the pc1-51-FLAG plasmid (encoding a 2.9-kDa protein) and the pc52-261-FLAG plasmid (encoding a 8.9-kDa protein), respectively. Sequencing to show that all the constructs did not have errors was performed by the method of Sanger et al. (7). □, FLAG sequence; ←, EcoRI site; ▸, XhoI site. (B) Expression of the prokaryotic constructs yielded the fusion protein p10-FLAG (lanes 1 and 2) and the FLAG-tagged p10 deletion mutation proteins (lanes 3 to 11). These were identified with the use of the anti-FLAG monoclonal antibody (Sigma) in Western blot analysis. The p10-FLAG protein was also identified with the use of anti-p10 serum in Western blot analysis. Alkaline phosphatase-conjugated protein A/G (A+G) (Pierce) and 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolylphosphate–nitroblue tetrazolium (BCIP-NBT) (Sigma) reactive to the alkaline phosphatase-conjugated protein A/G were used for the detection of the proteins. The 17-kDa His-S-p10-FLAG was identified by the anti-p10 serum (lane 1) and by the anti-FLAG monoclonal antibody (lane 2). The anti-FLAG monoclonal antibody also identified the His-S-tagged 10.1-kDa peptide 1-27-FLAG encoded by pET1-81-FLAG (lane 3), the 10.7-kDa peptide 28-59-FLAG encoded by pET82-177-FLAG (lane 4), the 10.2-kDa peptide 60-87-FLAG encoded by pET178-261-FLAG (lane 5), the 8.9-kDa peptide 1-17-FLAG encoded by pET1-51-FLAG (lane 6), the 8.7-kDa peptide 1-15-FLAG encoded by pET1-45-FLAG (lane 7), the 8.8-kDa peptide 1-16-FLAG encoded by pET1-48-FLAG (lane 8), the 15-kDa p10Δ17-FLAG encoded by pET52-261-FLAG (lane 9), the 16.9-kDa p10Δ2-FLAG encoded by pET7-261-FLAG (lane 10), and the 16.8-kDa p10Δ3-FLAG encoded by pET10-261-FLAG (lane 11).