Fig. 3.
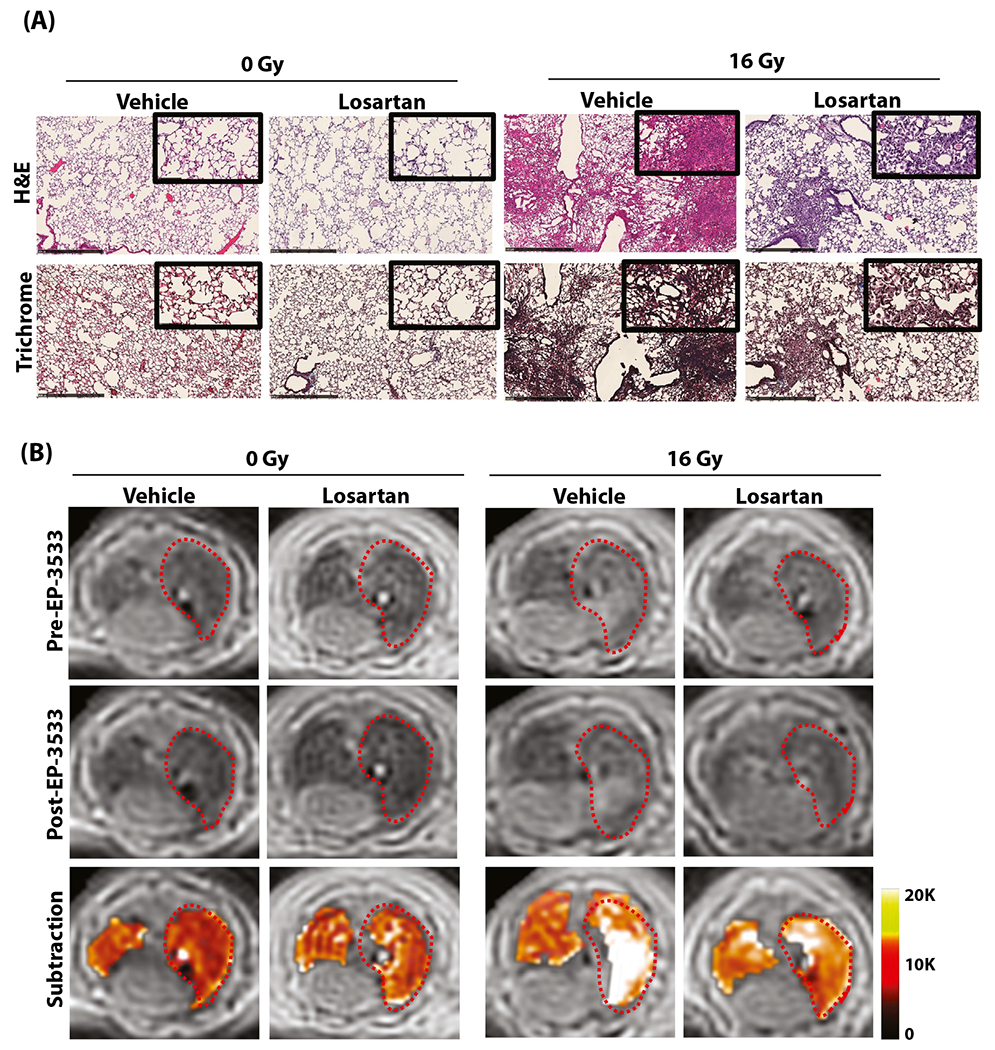
Mitigation of radiation-induced lung injury (RILI) with losartan in a murine model. (A) Representative hematoxylin and eosin (H&E; top) and trichrome (bottom) stains of the right lung show normal lung architecture in the 0-Gy groups, whereas the 16-Gy groups developed interstitial inflammation and alveolar thickening consistent with RILI, which is less severe in losartan-treated mice. (B) Representative axial magnetic resonance images before and after EP-3533 administration. Unirradiated (0-Gy) mice demonstrate low signal in both lungs, whereas irradiated mice demonstrate increased signal in the right lung consistent with RILI. Images acquired 40 minutes after EP-3533 administration (middle) show increased lung signal in the irradiated mice compared with the preinjection images, although signal enhancement is diminished in mice treated with losartan. False color subtraction images (40 minutes following EP-3533 injection — preinjection) overlaid on preinjection ultra-short echo time images demonstrate increased signal enhancement in the irradiated lung and decreased signal enhancement in mice treated with losartan.
