Fig. 4.
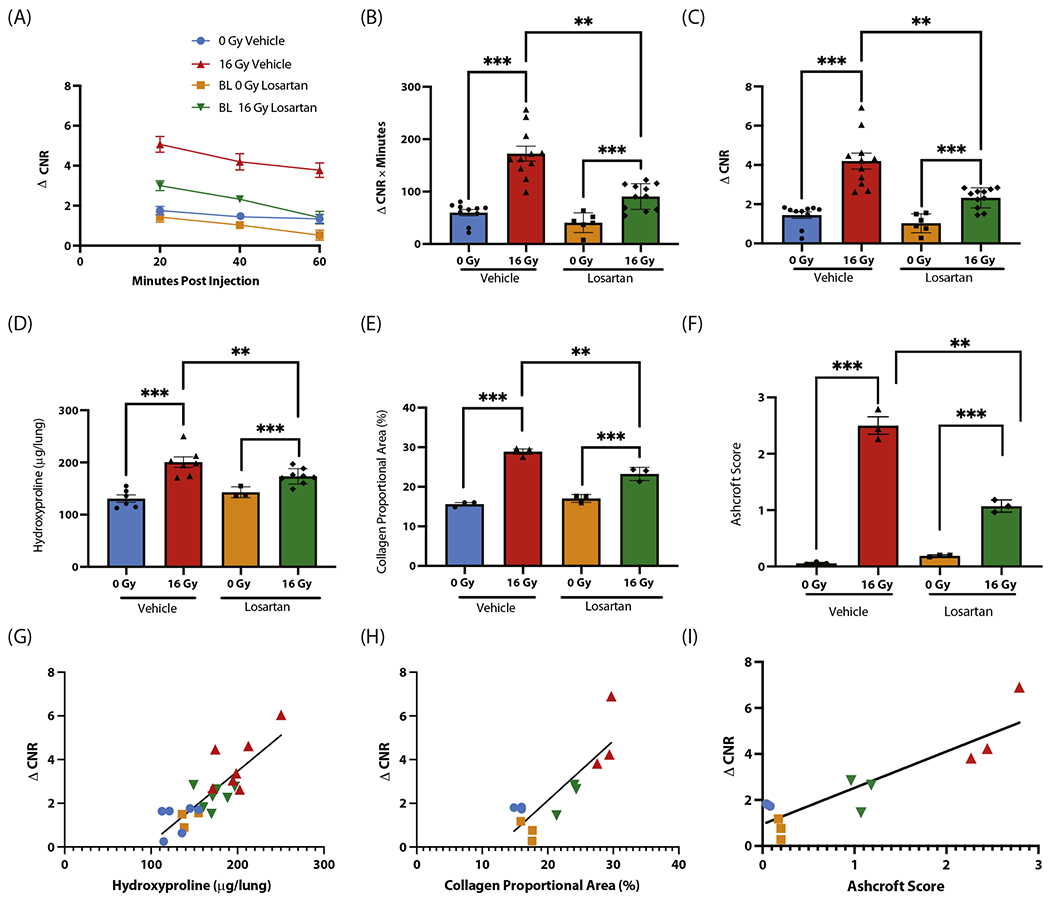
EP-3533 detects pharmacologic mitigation of radiation-induced lung injury with losartan in a murine model. (A) Change in contrast-to-noise ratio (ΔCNR) versus time curves demonstrate increased EP-3533 signal in the irradiated groups, although signal was reduced in the irradiated losartan group. (B, C) Area under the curve quantification (B) and ΔCNR at 40 minutes postinjection (C) revealed elevations in EP-3533 signal in the irradiated vehicle group, which was significantly reduced with losartan treatment. (D-F) Hydroxyproline (D), collagen proportional area (E), and Ashcroft score (F) each show significant increases with radiation, which are reduced in mice treated with losartan. (G-I) The associations between EP-3533 and hydroxyproline (G), collagen proportional area (H), and Ashcroft score (I) were assessed via Pearson correlation, and EP-3533 was significantly correlated with radiation-induced lung injury severity in each (*P < .05, **P < .001, ***P < .0001).
