Fig. 5.
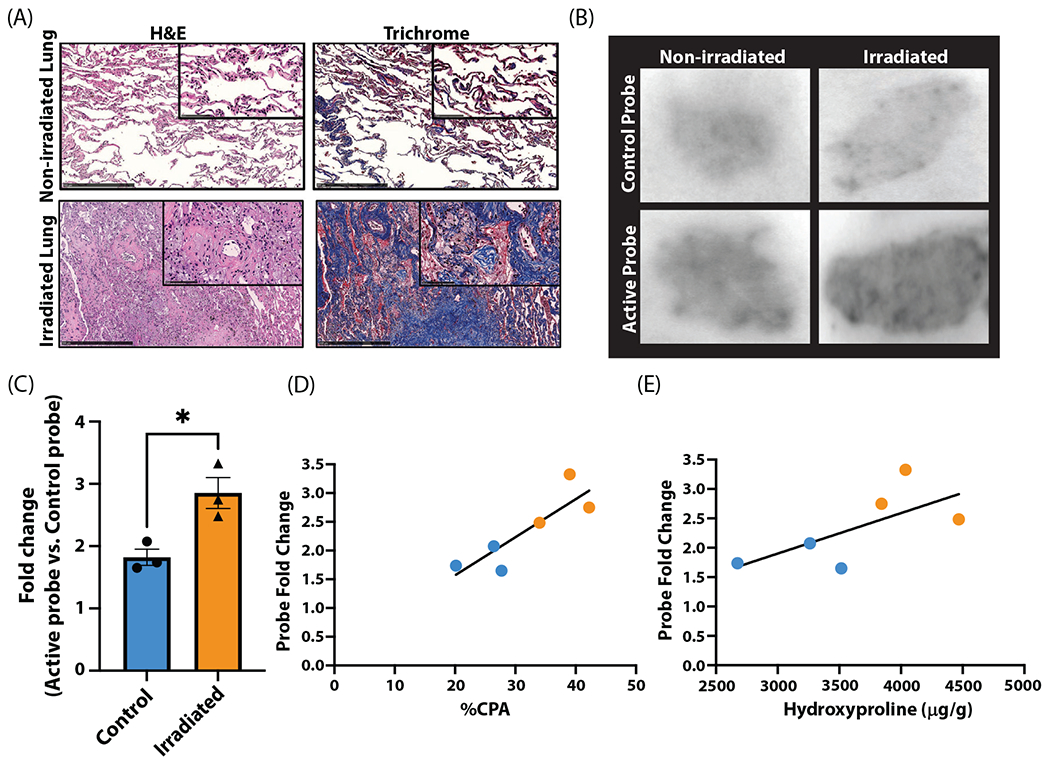
Quantification of 68Ga-CBP8 in human tissue with radiation-induced lung injury. (A) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E; left) and trichrome (right) stains of nonirradiated (top) and irradiated lung (bottom) with characteristic radiation-induced lung injury changes including cellular infiltration, alveolar wall thickening, and increased collagen deposition. (B) Autoradiography following incubation with 68Ga-Ctrl shows similar uptake between irradiated and nonirradiated lung tissue (top). 68Ga-CBP8 has increased uptake in irradiated versus nonirradiated lung tissue (bottom). (C-E) 68Ga-CBP8 intensity normalized to 68Ga-Ctrl signal intensity is significantly increased in irradiated tissue (P = .021; C) and is significantly correlated with collagen proportional area (CPA; P = .026; D) but not with hydroxyproline (E).
