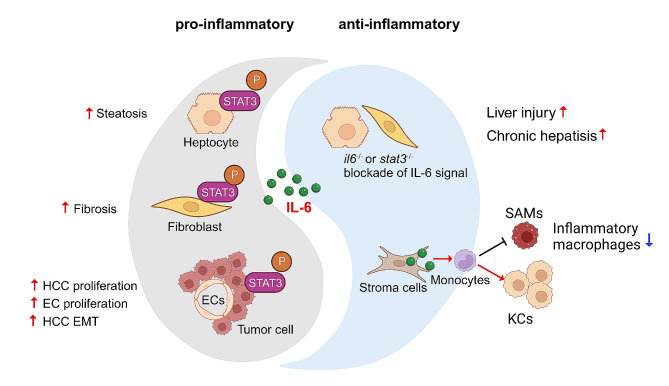
Fig. 4.
The pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory effects of IL-6 in the liver pathological process. The overexpression of IL-6 induced by liver injury presents a double-edged sword effect on the hepatic pathological process. Its pro-inflammatory effect promotes liver steatosis, fibrosis, endothelial cells (ECs) proliferation, and HCC development. On the other side, liver injury or chronic hepatitis are promoted in IL-6 or STAT3 knockout mice, suggesting the anti-inflammatory effect of IL-6. Moreover, IL-6 secreted by liver stroma cells can induce the differentiation of recruited monocytes towards tissue-resident Kupffer cells, but away from SAMs, so as to limit hepatic inflammation