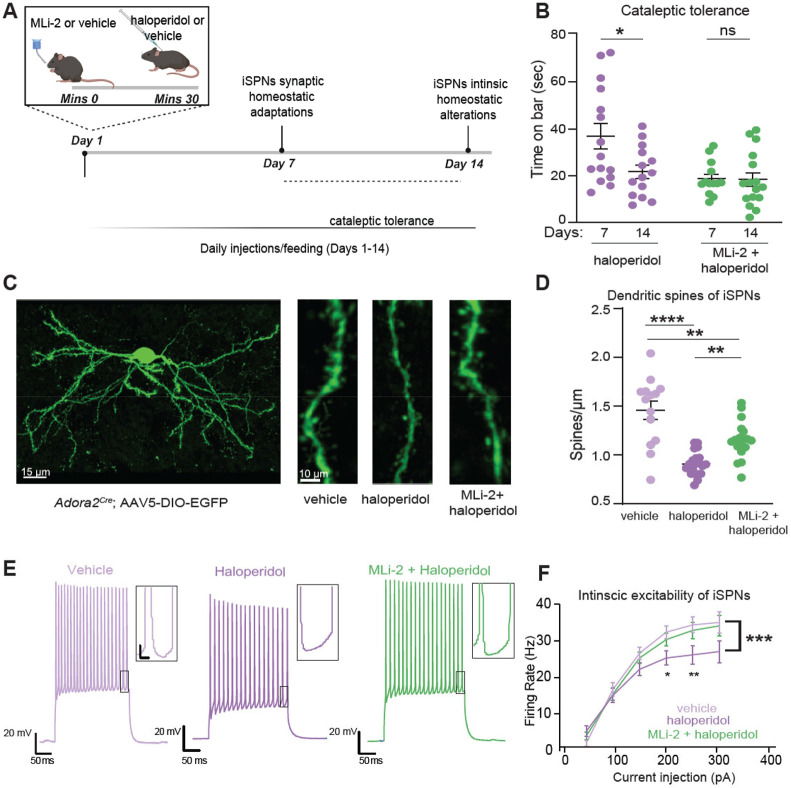
Figure 2. LRRK2 interferes with haloperidol induced adaptations in indirect pathway SPNs.
A. Schematic of the proposed timeline for synaptic and cell-intrinsic adaptations with haloperidol treatment, based on a synthesis of current and prior findings. Some of the schematics were created with BioRender.com.
B. Cataleptic response of WT mice receiving haloperidol, or haloperidol + MLi-2, at 7 and 14 days following treatments. Haloperidol-treated mice develop tolerance to catalepsy after 14 but not 7 days of haloperidol administration. N=15, 14, 13, 16 mice, in order of groups presented. Data for 7- and 14-day regimens are from panels 1B and Suppl. Fig. 1G, respectively.
C. Left, Example of confocal maximum projection image of an Adora2aCre SPN expressing AAV5/DIO-EGFP. Scale bar=15 μm. Right, Examples of dendritic segments in different treatment conditions. Scale bar=10 μm.
D. Summary graph of dendritic spine density in iSPNs across treatments. N=14-20 cells, 3 mice/group.
E. Example current clamp recording traces in response to a 150 pA current injection in iSPNs of WT mice after 14 days of treatment, as noted. Recordings were performed 24-48 hours after the final injection. Insets: scale 4 mV, 20 ms.
F. Summary data show decreased cellular excitability with haloperidol, rescued to control levels by LRRK2 inhibition. Scale, as noted. N=14-29 cells, 4-6 mice/condition.
Data are represented as mean±SEM. Asterisks in B show statistical significance for Tukey's multiple comparison tests after two-way ANOVA; *p< 0.05. D shows statistical significance for Tukey's multiple comparison tests after one-way ANOVA**p< 0.01, ****, p<0.0001. Asterisks in F show statistical significance after two-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons. Large asterisk, interaction between treatment and current steps. Small asterisks, significance at specific current steps, determined by Sidak multiple comparisons. *p<0.05.