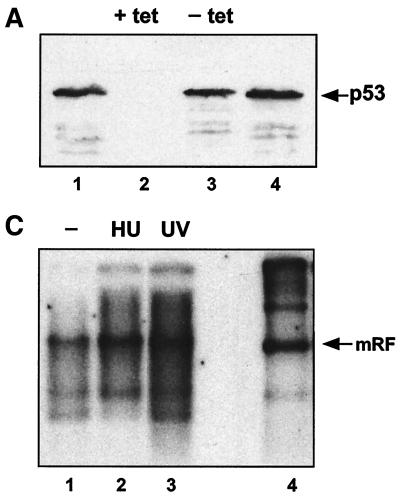
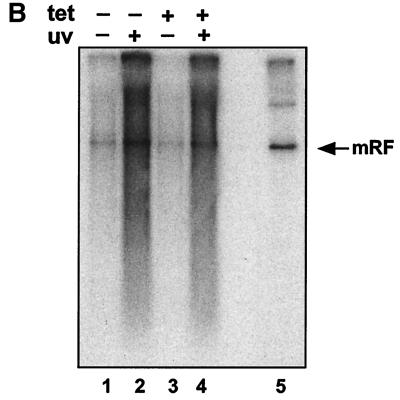
FIG. 4.
(A) Tetracycline-repressible p53 expression in H1299. H1299p53 cells were seeded at approximately 3 × 106 cells/dish and grown for 48 h in the presence (+ tet) or absence (− tet) of tetracycline. At this time point, two plates (one with and one without tetracycline) were harvested. (The remaining plates were used to test the ability of these cells to amplify AAV DNA in response to UV [see panel B].) The two harvested plates were analyzed for the presence of p53 using SDS-polyacrylamide gels and Western blotting using 1/12 of the extract from each dish. Lanes 1 and 4, HaCat cell extract as a positive control for p53 detection. Lanes 2 and 3, H1299p53 in the presence (lane 2) or absence (lane 3) of tetracycline. (B) The AAV DNA amplification response to UV irradiation is independent of expression of p53 in H1299 cells. H1299p53 cells were used to test for dependence of UV-induced AAV DNA amplification on p53 expression level. Plates cultured in parallel with those used for panel A, in the presence (tet +) or absence (tet −) of tetracycline, were either treated with UV or left untreated. All plates were then infected with AAV. On the third day postinfection, total DNA was extracted and 5 μg/sample was analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis and Southern blotting. Lanes 1 and 2, AAV-infected H1299p53 cultured in the absence of tetracycline; lane 1, no UV irradiation; lane 2, cells were UV irradiated. Lanes 3 and 4, AAV-infected H1299p53 cultured in the presence of tetracycline; lane 3, no UV irradiation; lane 4, cells were UV irradiated. Lane 5, marker DNA for AAV replication in the presence of adenovirus. (C) p53-null cells can amplify AAV DNA in response to UV irradiation. Approximately 2 × 106 cells of the H24 clone of H1299 cells (which lack the p53 expression construct) per dish were either treated with 1 mM hydroxyurea (Sigma) for approximately 24 h prior to infection or, immediately prior to infection, treated with UV. These plates and a control untreated plate were then infected with AAV, and at 24 h postinfection, total DNA was extracted and 5 μg/sample was analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis and Southern blotting. Lane 1, AAV-infected H24 cells. Lanes 2 and 3, H24 cells infected as described for lane 1 but with either hydroxyurea (HU) (lane 2) or UV irradiation (lane 3) pretreatment of the cells. Lane 4, marker DNA for AAV replication in the presence of adenovirus. mRF, monomer replicative form.