Figure 2. Incorporation of an anti-Cluster I mAb substantially improves the capacity of anti-cluster A/anti-CoRBS to mediate ADCC in presence of CD4mc.
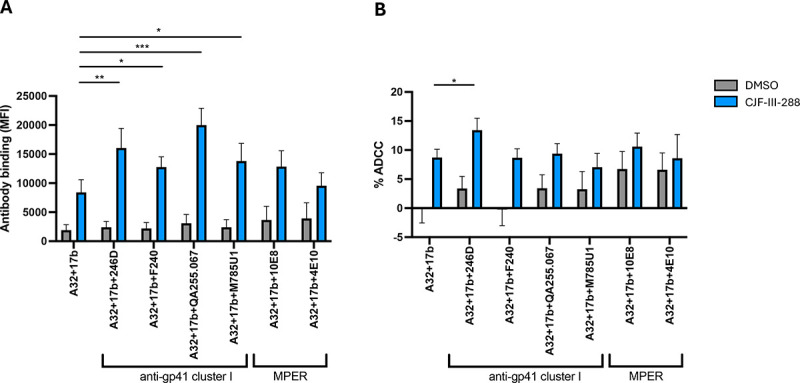
(A) HIV-1CH058TF-infected primary CD4 T cells were stained with a total 5μg/mL of indicated combination of nnAbs in presence of CJF-III-288 depicted in blue or DMSO depicted in gray 48h post-infection. Flow cytometry was performed to detect antibody binding using appropriated secondary antibody. The graph represents the mean fluorescence intensities (MFI) of Alexa-Fluor 647 obtained in at least 5 independent experiments. (B) HIV-1CH058TF-infected primary CD4 T cells were as target cells, while autologous non-infected PBMCs were used as effector cells in our FACS-based ADCC assay in the presence of 5μg/mL of indicated combination of nnAbs. The graph represents the percentage of ADCC obtained in presence of indicated combination of antibodies in at least 5 independent experiments. Statistical significance was tested using (A-B) Mixed-effects analysis (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001; ns, nonsignificant).
