Figure 3. A cocktail comprising 17b, A32, 246D and CJF-III-288 mediates potent ADCC.
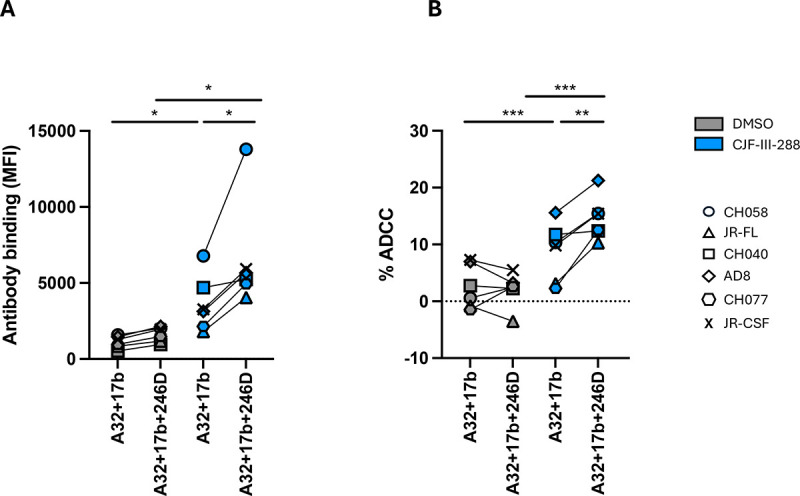
(A) Primary CD4+ T cells were infected with indicated primary viruses. At 48 h post infection, cells were stained with a total 5 μg/mL of indicated antibody combination in presence of CJF-III-288 depicted in blue or DMSO depicted in gray. Flow cytometry was performed to detect antibody binding using Alexa-Fluor 647 conjugated anti-human secondary antibody. The graph represents the MeanFI of Alexa-Fluor 647 obtained in at least 3 independent experiments with each virus. Each virus is depicted as a different symbol. (B) Primary CD4+ T cells infected with indicated viruses were used as target cells, while autologous non-infected PBMCs were used as effector cells in our FACS-based ADCC assay in the presence of a total of 5 μg/mL of indicated combination of nnAbs. The graph represents the mean percentage of ADCC obtained from each virus in at least 3 independent experiments. Each virus is depicted as a different symbol. Statistical significance was tested using (A-B) paired t-tests or Wilcoxon tests based on statistical normality (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01).
