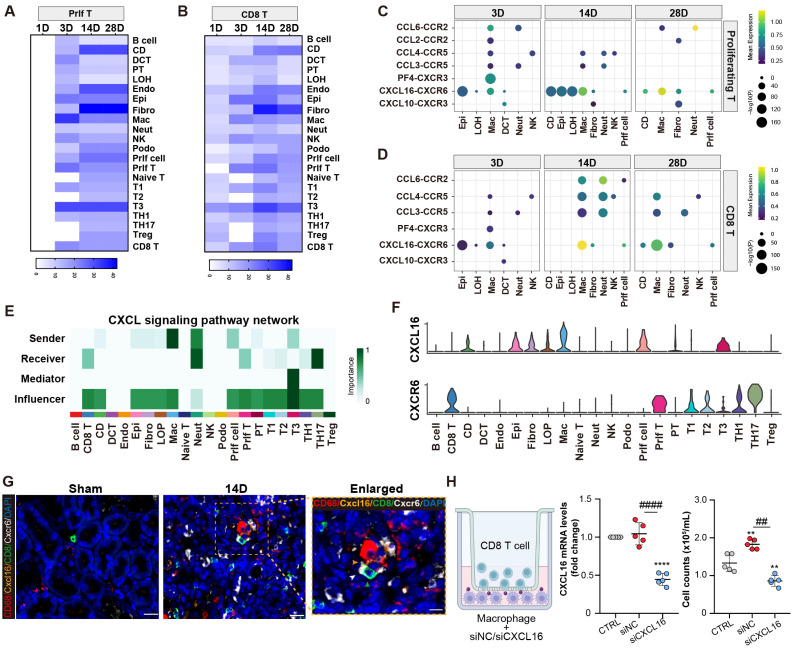
Figure 4.
Proliferating/CD8 T cluster is recruited by macrophages through Cxcl16-Cxcr6 signaling. (A-B) The interaction numbers between proliferating/CD8 T subtypes and other cells at each time point. (C-D) Enriched numbers of cytokine and chemokine signaling pathway interactions between other cells and proliferating/CD8 T subtypes. (E-F) Enriched CXCL signaling pathway networks and the significant ligand-receptor pair CXCL16-CXCR6 between macrophages and CD8 T cluster are depicted (CD: collecting-duct; DCT: distal convoluted tubule; PT, proximal tubule; LOH: loop of Henle; Endo: endothelial cell; Epi: epithelial cell; Fibro: fibroblast; Mac: macrophage; Neut: Neutrophil; NK: natural killer Cell; Podo: podocyte; prlf cell: proliferation cell.). (G)Representative immunofluorescence images of the spatial distribution of CXCL16, CD68 positive macrophages alongside CXCR6 positive CD8 T cells. (H) A co-culture system was applied to evaluate the migration capacities of the CD8 T cell cluster when affected by macrophages transfected with CXCL16 siRNA or NC siRNA. The number of migrated CD8 T cells in the lower chamber was quantified. Scale bars, 20μm (Enlarged Scale bars, 10μm.). Data are presented as means ± SD.**P<0.01, **** P < 0.0001, compared to the control group; ## P<0.01, #### P<0.0001, compared to macrophages transfected with NC siRNA group.