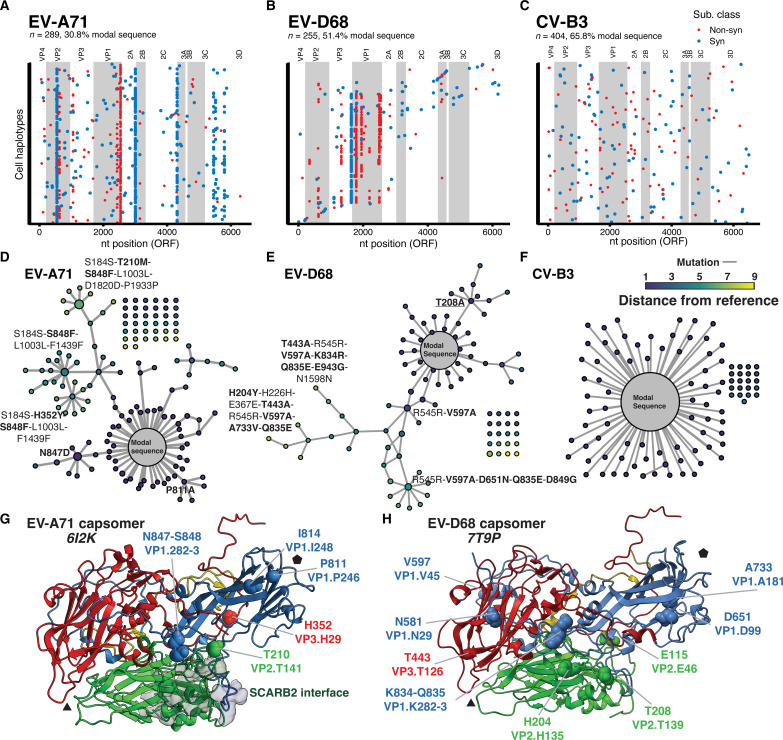
Fig. 2. Population dynamics across the EV-A71 genotype network.
(A to C) SEARCHLIGHT-derived haplotypes of three populations of EV-A71, EV-D68, and CV-B3. Color indicates whether mutations were non-synonymous or synonymous. Viral gene products within the viral polyprotein are labeled and denoted by alternate shading. ORF, open reading frame. (D to F) The same SEARCHLIGHT-derived genotypes, shown as genotypic networks. Each node represents a genotype, with size representing the relative frequency of the genotype. Edges represent single-nucleotide substitutions linking individual genotypes. The unconnected dots are detected genotypes within the sample that are not directly connected through mutation to the modal sequence via other observed genotypes. While the EV-A71 and EV-D68 populations are derived from stocks generated by long-term propagation, the CV-B3 population is derived from a molecular clone. (G and H) Structures of a single homooligomeric monomer of the (G) EV-A71 and (H) EV-D68 capsid, known as a capsomer. The most frequent mutations found on the recovered haplotypes are highlighted on the structure and colored by subunit. The black triangle and pentagon indicate the three- and fivefold axes, respectively.