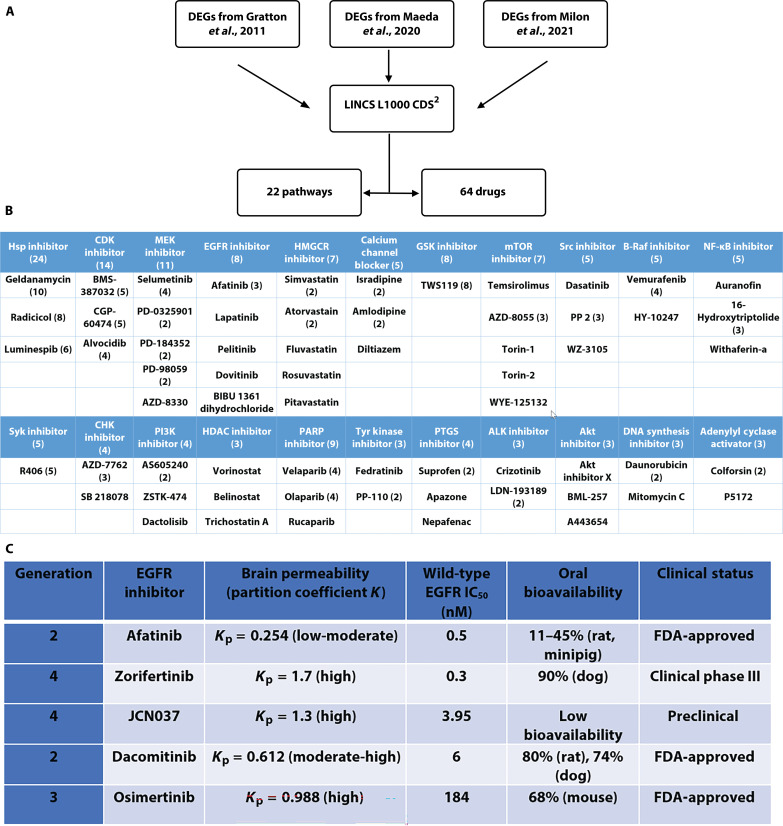
Fig. 1. In silico screening identifies protective pathways and drugs against NIHL.
(A) Workflow on in silico screens for pathways and drugs to protect against NIHL. (B) Top biological pathways and drug candidates identified against NIHL. HSP, heat shock protein; CDK, cyclin-dependent kinase; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; HMGCR, 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase; GSK, glycogen synthase kinase; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; CHK, checkpoint kinase 1; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; HDAC, histone deacetylase; PAPR, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase; PTGS, prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase; ALK, anaplastic lymphoma kinase. (C) EGFR inhibitors with proper safety and pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics profiles. IC50, median inhibitory concentration.