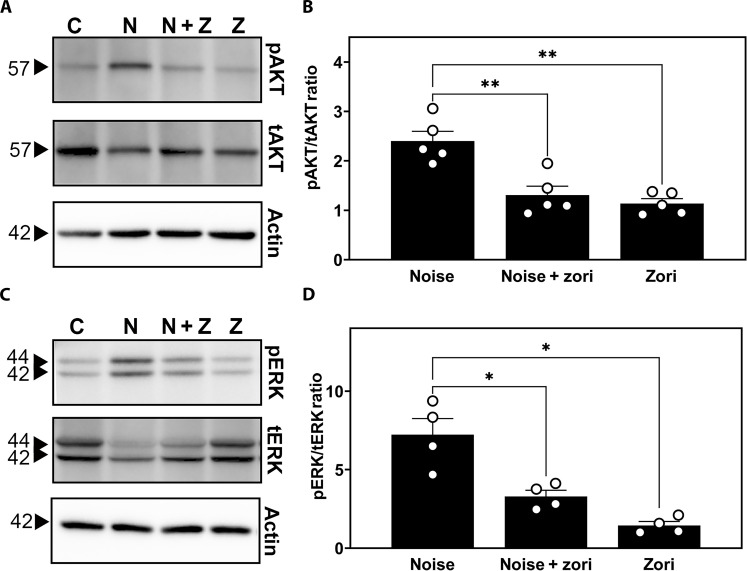
Fig. 7. EGFR signaling is activated in the mouse cochlea following noise exposure and attenuated by zorifertinib.
(A to D) Western blotting was performed on organ of Corti lysates from mice 30 min after exposure to noise trauma (8- to 16-kHz noise band at 100-dB SPL for 2 hours) and pretreated with either the drug (zorifertinib 15 mg/kg, oral) or the vehicle (normal saline or methyl cellulose) 1 day before and 1 hour during the noise trauma to detect the phosphorylation status (p, phosphorylated versus t, total) of two downstream effectors of EGFR (AKT and ERK). Zorifertinib pretreatment significantly decreased the noise-induced increase of AKT and ERK phosphorylation. [(A) and (C)] The sizes of the bands are labeled in kilodaltons. C, untreated and unexposed control; V + N, vehicle + noise; Z + N, zorifertinib + noise; Z, zorifertinib only. Actin: A loading control. [(B) and (D)] Ratios of phosphorylated versus total proteins normalized to actin loading controls. Data are normalized to untreated/exposed control mice as a ratio of 1 and presented as means ± SD. N = 4 to 5 biological replicates and each dot represents one mouse in each group. ANOVA, Tukey’s post hoc. *P ≤ 0.05 and **P ≤ 0.01.