Fig. 2. Extracellular and intracellular self-nucleic acids.
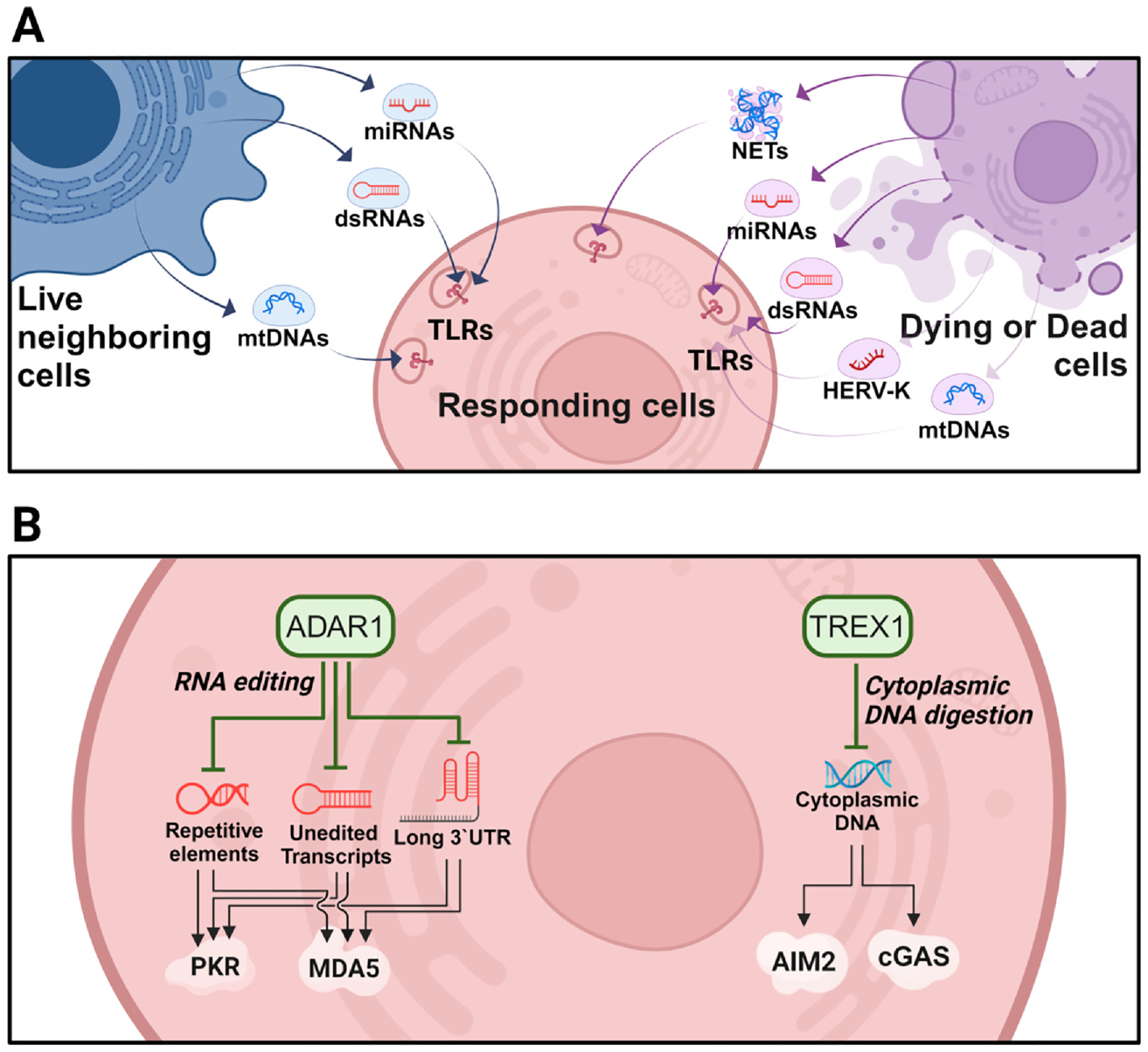
(A) Extracellular nucleic acids originating from neighboring live, dead, or dying cells. Released miRNAs, dsRNAs, HERV-K, mtDNA, and NETs can activate TLRs (TLR3, 7/8, and −9) in nearby responding cells. (B) Intracellular nucleic acids originating from the loss of regulators within cells. ADAR1 and TREX1 are major regulators of immunostimulatory self-RNA and self-DNA nucleic acids, respectively. Loss of these regulatory mechanisms can lead to hyperactivation of various PRRs and promotes neurodegeneration.
