Figure 2. Targeted scRNA-seq and reference mapping analysis of one patient with HMF indicates a malignant CD4+ T-cell population separate from clonal CD8+ T cells.
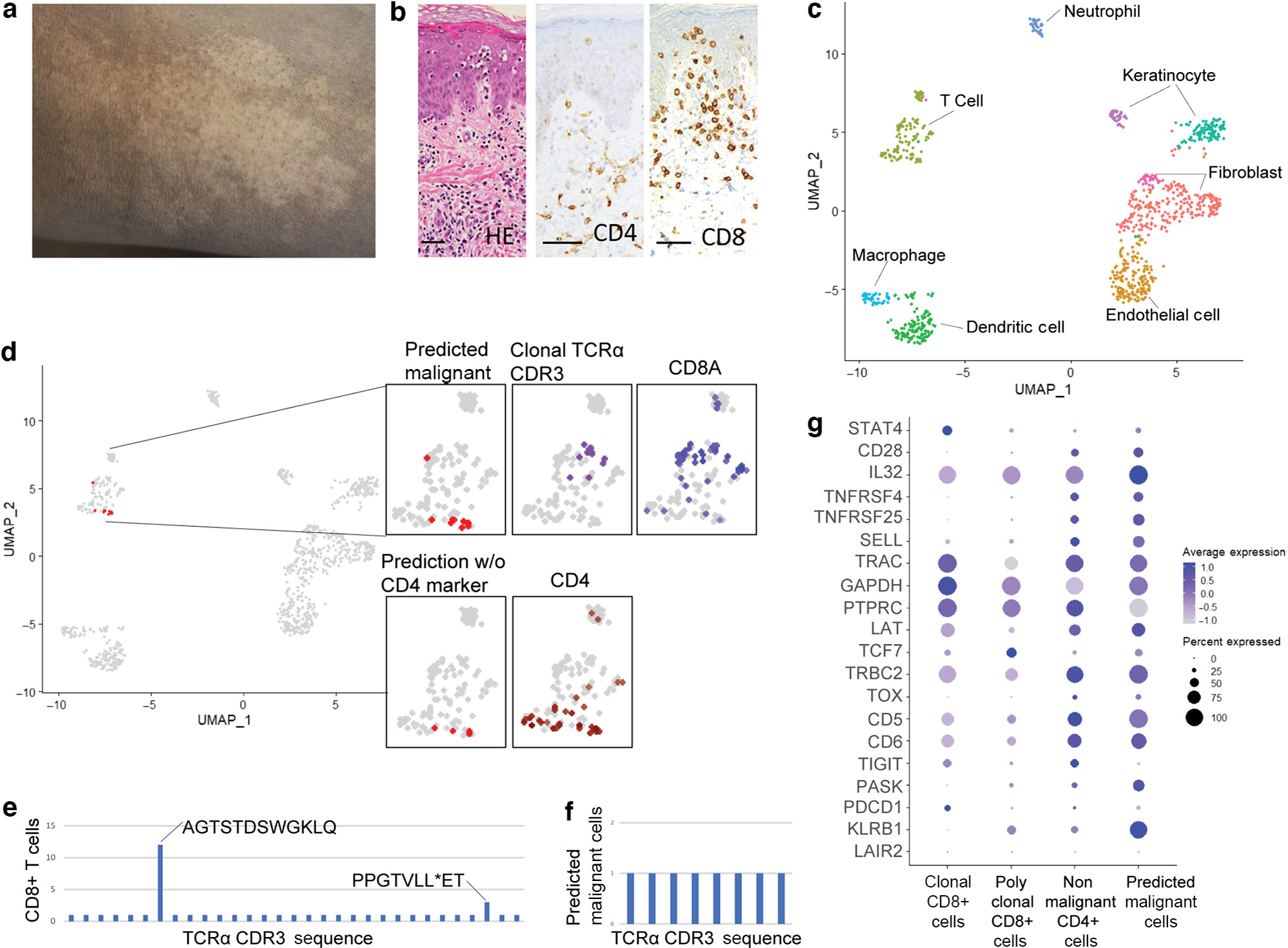
(a) Hypopigmented patch. (b) Atypical CD8+ epidermotropic lymphocytes on skin biopsy (H&E, CD4, and CD8 staining; bar = 50 μm). (c) UMAP projection of scRNA-seq from a patient with HMF. (d) Reference mapping prediction of malignant cells in a patient with HMF using model built on GSM5280111. Clustering of clonal T cells, CD4+ T cells, and CD8+ T cells are also shown. (e) TCR-α CDR3 amino acid sequences in CD8+ T cells. (f) TCR-α CDR3 amino acid sequences in predicted malignant T cells. (g) Dot plot of the top 20 differentially expressed genes used in the reference mapping model showing gene expression in clonal CD8+ T cells, polyclonal CD8+ T cells, nonmalignant CD4+ T cells, and predicted malignant cells in the patient with HMF. HMF, hypopigmented mycosis fungoides; scRNA-seq, single-cell RNA sequencing; STAT4, singal transducer and activator of transcription 4; UMAP, Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection.
