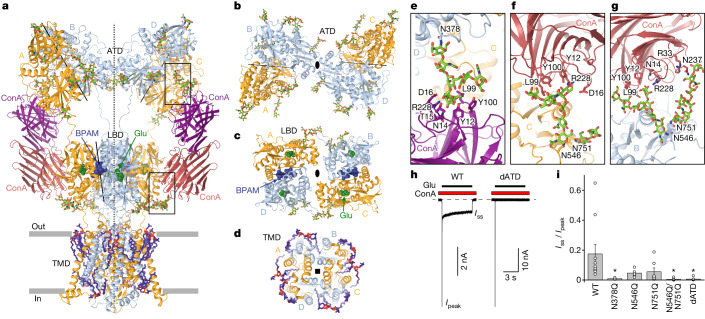
Fig. 2. The structure of GluK2Glu–ConA–BPAM.
a, The GluK2Glu–ConA–BPAM structure viewed parallel to the membrane, with subunits A and C coloured orange, B and D in light blue, and ConA in purple and magenta. Glu (dark green) and BPAM (dark blue) are shown as space-filling models. Carbohydrates (light green) and lipids (violet) are shown as sticks. The axes of the two-fold overall symmetry and local symmetry of the ATD and LBD dimers are shown as dashed and solid black lines, respectively. Boxed regions are expanded in e–g. b–d, Extracellular views of ATD (b), LBD (c) and TMD (d) layers. e–g, ATD–ConA (e) and LBD–ConA type I (f) and II (g) interfaces, with glycosylated asparagines and ConA residues in contact with carbohydrates shown as sticks. h, Whole-cell patch-clamp currents recorded at –60 mV membrane potential from HEK 293F cells expressing wild-type (WT) or dATD GluK2 in response to a 6-s application of 3 mM Glu in the continuous presence of 0.3 mg ml−1 ConA. Ipeak, peak current; Iss, steady-state current. i, Steady-state to peak current ratio for wild-type and indicated mutant GluK2 channels. Data are mean ± s.e.m. Biologically independent measurements: n = 10 for wild type, n = 6 for N378Q, n = 5 for N546Q, n = 7 for N751Q, n = 10 for N546Q/N751Q and n = 8 for dATD. Data are representative of five independent experiments. Two-sided two-sample t-test, *P < 0.05. P = 0.029 for N378Q, P = 0.078 for N546Q, P = 0.109 for N751Q, P = 0.026 for N546Q/N751Q and P = 0.027 for dATD.