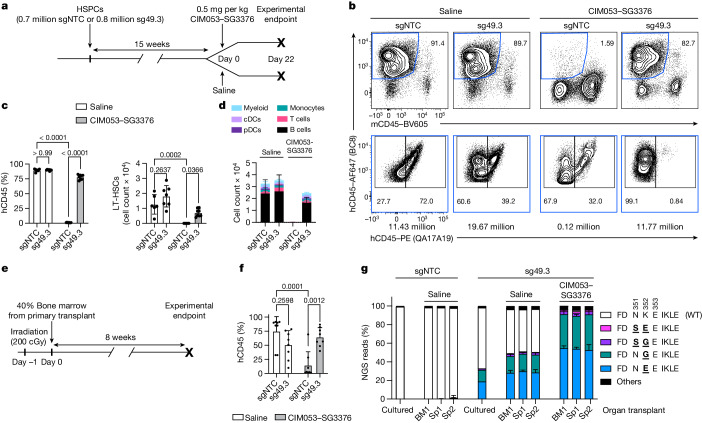
Fig. 3. Engineered HSPCs retain function and are shielded from CIM053–SG3376 in vivo.
a, Experimental timeline of NBSGW primary host mice (4 weeks old) humanized with control (sgNTC) or edited (sg49.3) HSPCs. Mice were subsequently treated with saline or CIM053–SG3376. b, Flow-cytometry analysis depicting the percentage of human chimerism (BC8+mCD45−) (top row, blue gate) in the BM of mice 22 days after treatment. Percentage of edited (BC8+QA17A19−) and unedited (BC8+QA17A19+) cells in the human cell population (bottom row). Absolute cell counts of representative panels, calculated according to input counting beads, are shown below each panel. c, Quantification of human chimerism (BC8+mCD45−) and LT-HSCs (BC8+mCD45−CD34+CD38−CD90+CD45RA−) in the BM of all mice. Selected P values are shown. d, Multi-lineage differentiation in the blood of all animals (conventional dendritic cells (cDCs); plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs)). e, Experimental timeline of secondary transplant in NSG–SGM3 host mice (4 weeks old). f, Quantification of human chimerism (BC8+mCD45−) in the BM of secondary host mice. Selected P values are shown. g, NGS of matching electroporated cells cultured in vitro and organs from primary (bone marrow, BM; spleen, Sp1) and secondary (spleen, Sp2) host transplants. NGS reads accounting for less than 0.8% of total reads were classified as ‘others’ (n = 6–8 mice per group in a–f, 8 mice per group in g; data are mean ± s.d.). Ordinary two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) tests (significance level, α = 0.05) were used to assess statistical difference between groups.