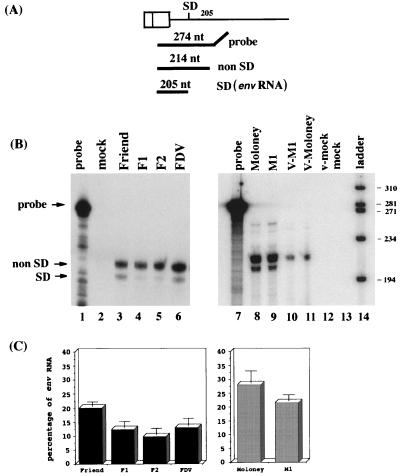
FIG. 6.
Quantification by RNase protection of the canonical env transcript level in MuLV-infected cells. (A) Friend and Moloney transcripts were detected by RNase protection with the uniformly labeled antisense SPFLV or SPMLV probes, respectively (see Materials and Methods), which overlap the canonical SD site. Hybridization of the 274-nt probe to viral RNA species that are not spliced at the canonical SD site (full length, SD′, and SD" RNA) yields a protected 214-nt fragment, while canonically spliced env RNA yields a protected 205-nt fragment. (B) RNase protection assays were carried out with 15 μg of total cellular RNA (lanes 2 to 6, 8, 9, and 13) and RNA extracted from 10% total virus pelleted medium from infected or mock-infected cell monolayers (lanes 10 to 12). The positions of the probe and the protected fragments corresponding to canonically spliced env RNA (SD) as well as the noncanonically spliced RNAs (non SD) are indicated by arrows. The size markers (lane 14) consist of end-labeled φX174 HaeIII DNA fragments. (C) Quantification of RNase protection assays. For each series, the percentage of env-protected fragments versus the total of protected signals is represented (± standard of the mean). Each value corresponds to the average of at least three measurements performed on different RNA preparations.