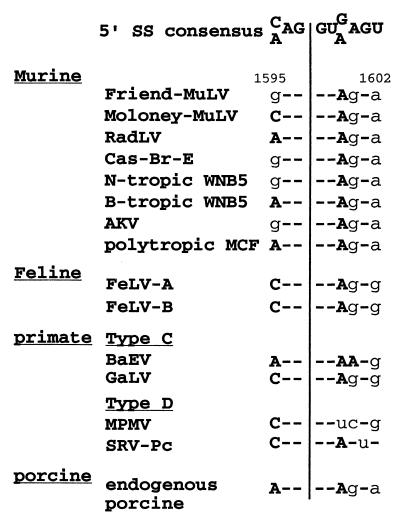
FIG. 7.
Conservation of the SD′ site. Sequence alignment of a putative SD′ site in the capsid-coding region of a series of replication-competent mammalian types C and D retroviruses. The 5′ splice donor site consensus sequence (5′ SS) is shown on top, with the potential splicing cleavage site indicated by a vertical line. All sequences were located approximately 100 nt upstream of the capsid major homology region. Numbering is according to the Friend-MuLV 57 sequence. Lower-case letters indicate mismatches between the 5′SS consensus and the viral sequence. Abbreviations and strains correspond to the following retroviruses. (i) MuLVs: Friend-MuLV, strain 57; Moloney-MuLV, strain 8.2; RadLV, radiation leukemia virus; Cas-Br-E, Lake Casitas brain E neurotropic virus; WNB5, the N- and B-tropic clones of the WN1802 isolate; and AKV, from clone AKR 623 of endogenous virus from the AKR mouse strain. All of the above are ecotropic MuLVs. MCF, clone MCF1233 of the polytropic mink cell focus-inducing viruses. (ii) Feline leukemia viruses: FeLVA and FeLVB, strains A and B. (iii) Primate simple retroviruses: simian type C retroviruses include BaEV, baboon endogenous virus, and GaLV, gibbon ape leukemia virus. Simian type D retroviruses include MPMV, Mason-Pfizer monkey virus, and SRV-Pc, a baboon simian retrovirus-like isolate. (iv) Porcine endogenous virus: a human-tropic C-type porcine endogenous retrovirus.