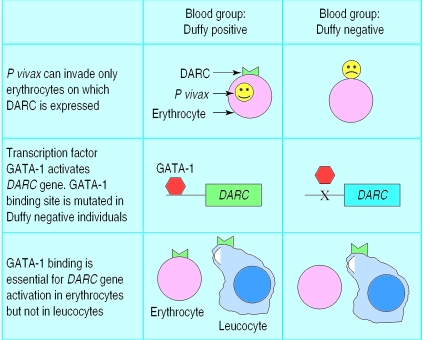
Figure 2.
The malaria parasite Plasmodium vivax invades human erythrocytes by binding to Duffy antigen/chemokine receptor (DARC) expressed on the erythrocyte surface. Many west Africans have a single nucleotide polymorphism in the DARC promoter region that prevents binding of the erythroid transcription factor GATA-1, thus suppressing DARC expression in erythrocytes but not other cell types. This confers complete protection against infection with P vivax but not against other species of malaria parasite, which invade erythrocytes through different receptors23,24