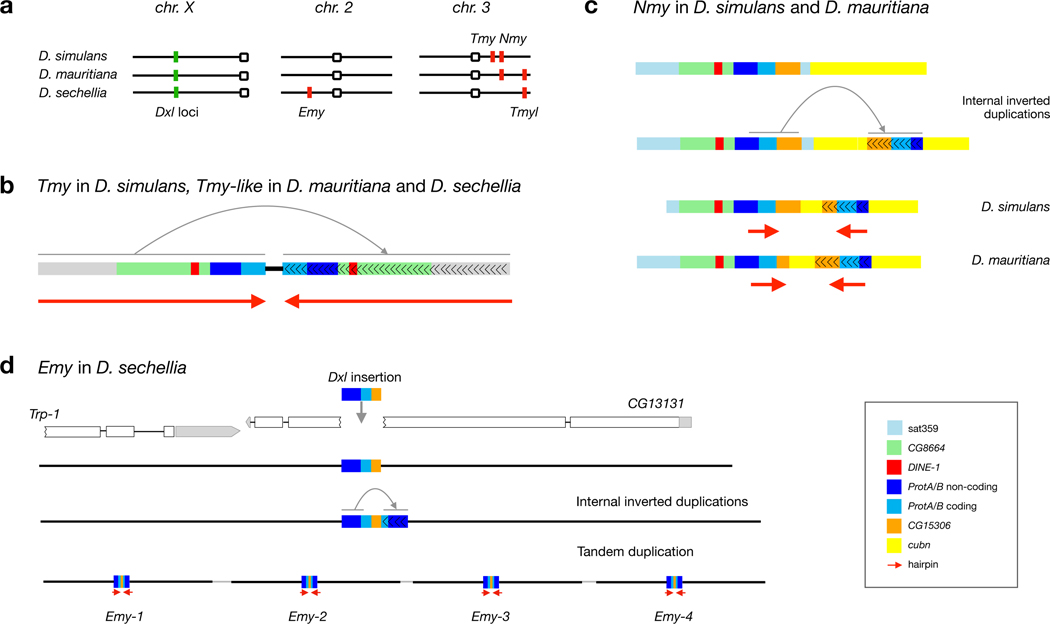
Figure 5.
Autosomal hpRNA suppressor loci in the D. simulans clade species. a. The three species have different, partially overlapping systems of Dxl genes and esiRNA-producing autosomal suppressors. D. simulans has Tmy and Nmy; D. mauritiana has Nmy and Tmyl; and D. sechellia has Tmyl and Emy. Structural features of the esiRNA-producing putative autosomal suppressors, Tmy and Tmyl (b), Nmy (c), and Emy (d). Each putative suppressor originated via the insertion of Dxl material into an autosomal location followed by internal duplication and inversion of sequence (gray arrows), allowing formation of hpRNA precursor molecules (red arrows). In D. sechellia, a ~7-kb region that includes Emy has been tandemly amplified four times (d).