Fig. 11.
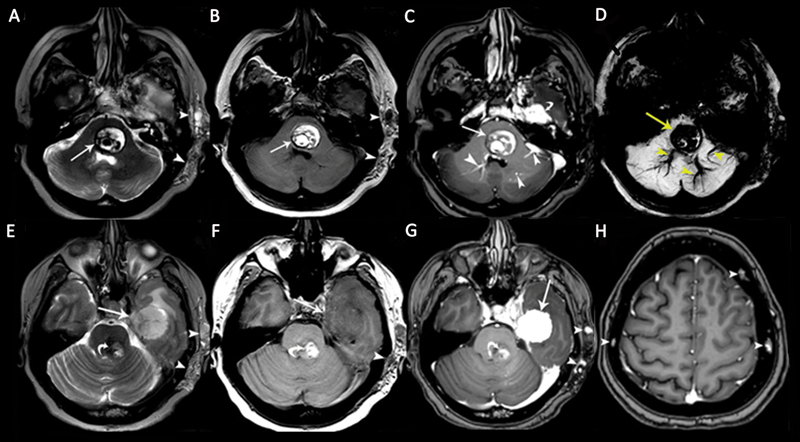
A 48-year-old woman patient with multiple cavernous malformations (CMs) associated with a cavernous sinus hemangioma. Axial (A) T2-weighted image (T2WI) and (B) T1-weighted image (T1WI) show a pontine CM with heterogeneous signals and peripheral hemosiderin deposits ( arrows ) associated with soft-tissue hemangioma in the left temporal subcutaneous area ( arrowheads ). (C) Contrast-enhanced axial T1WI shows nonenhancing CM ( arrow ), enhancing developmental venous anomalies (DVAs; arrowheads ) in the brainstem, and an enhancing dural cavernous hemangioma in the left middle cranial fossa ( curved arrow ). (D) Pontine CM and DVAs show “blooming artifacts” on susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI). (E) Axial T2WI shows a large dural cavernous hemangioma in the left middle cranial fossa with heterogeneous hyperintense signals ( arrow ). There is also a brainstem CM ( curved arrow ) and a soft-tissue hemangioma in the left temporal subcutaneous area ( arrowheads ). (F) The dural cavernous hemangioma in the left middle cranial fossa is hypointense on the axial T1WI. The soft-tissue hemangioma in the left temporal subcutaneous tissue is hypointense on the image ( arrowhead ). (G) The dural cavernous hemangioma in the left middle cranial fossa shows intense homogeneous enhancement on contrast-enhanced T1WI ( arrow ). The brainstem CM shows no enhancement ( curved arrow ). Soft-tissue hemangioma in the left temporal subcutaneous tissue shows a few dotlike enhancing areas, representing dilated veins. (H) Axial contrast-enhanced T1WI shows multiple calvarial CMs ( arrowheads ).
