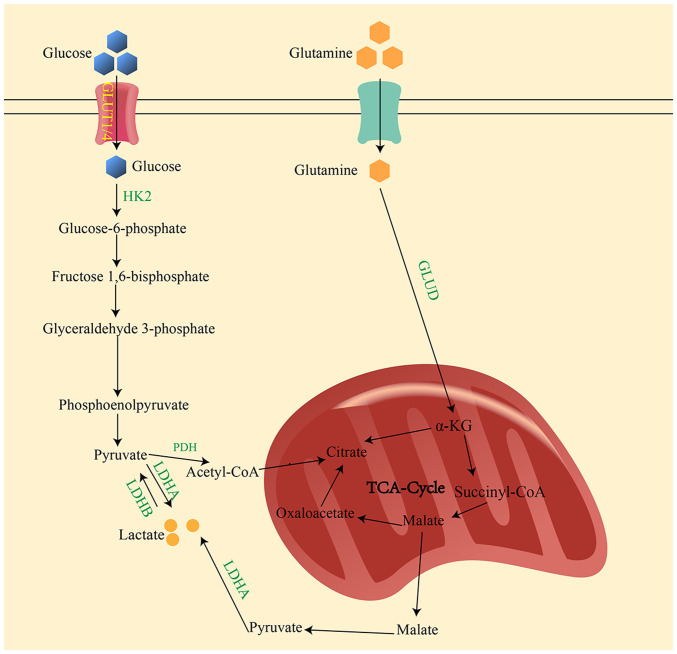
Figure 1.
Main production pathway of lactate. In the cytoplasm, glucose is converted to pyruvate through a series of catalytic reactions. Under normal oxygenation, pyruvate is transported to the mitochondria for the TCA cycle. However, under hypoxic conditions, pyruvate is catalyzed by LDHA to lactate. Glutamate is converted to α-ketoglutarate by GLUD in the mitochondria. Subsequently, α-KG is converted to malate, which is then transported out of the mitochondria and oxidized to pyruvate in the cellular matrix. Finally, lactic acid is produced by the action of LDHA. GLUT1/4, glucose transporter 1/4; HK2, hexokinase 2; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; LDHA/B, lactate dehydrogenase A/B; TCA, tricarboxylic acid; GLUD, glutamate dehydrogenase; α-KG, α-ketoglutarate.