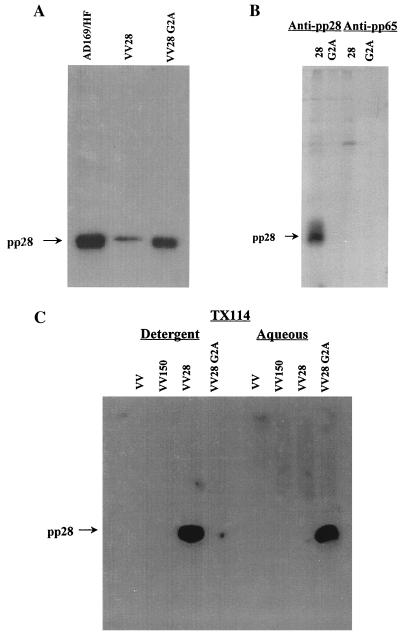
FIG. 2.
The membrane association of pp28 is dependent on myristoylation. (A) The G2A mutant pp28 is expressed in recombinant vaccinia virus-infected cells. BHK cells were infected with a recombinant vaccinia virus encoding wild-type pp28 (VV28) or the G2A mutant pp28 (VV28 G2A), and infected cell proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting using a pp28-specific MAb to develop the membranes. As a control, infected cell proteins from AD169-infected cells were also analyzed in an identical manner. The migration of pp28 is shown in the left margin. (B) The G2A pp28 mutation prevents myristoylation of pp28. BHK cells were infected with the recombinant vaccinia viruses encoding either pp28 or the G2A pp28 mutant and radiolabeled with [3H]myristic acid as described in the legend to Fig. 1. Infected cell proteins were then immunoprecipitated with either a pp28- or pp65 (UL83)-specific MAb and analyzed by SDS-PAGE. The migration of pp28 is shown in the left margin. (C) Myristoylation of pp28 is required for membrane association. BHK cells infected with wild-type (VV) or recombinant vaccinia viruses encoding pp150 (UL32, VV150), pp28, or the G2A mutant pp28 were partitioned by TX114 into a aqueous or detergent fraction as described in the legend to Fig. 1. The different fractions were then analyzed by immunoblotting, and the membranes were developed with a pp28-specific MAb. The migration of pp28 is shown in the left margin.