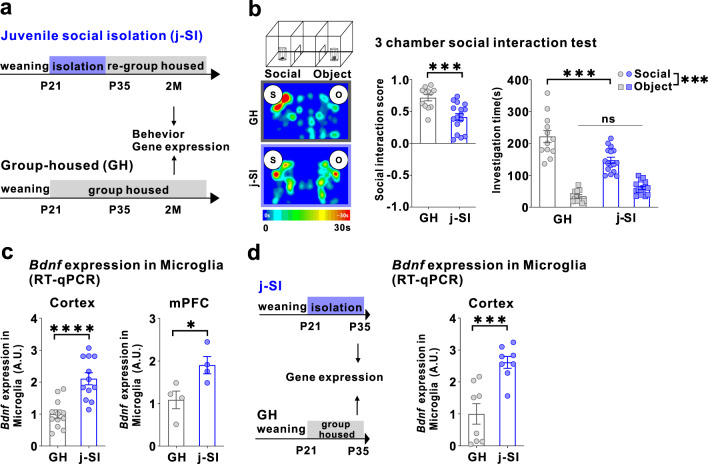
Fig. 1. Juvenile social isolation reduces sociability and increases MG-Bdnf expression.
a Schema of the group-housed (GH) and juvenile social isolation (j-SI) mice time series. The experiments started at p56. b j-SI mice displayed reduced sociability in the three-chamber sociability test compared with GH mice. j-SI mice had a lower social interaction score than GH mice (t(26) = 3.948, p = 0.0005, unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test, GH: n = 12, j-SI: n = 16) and spent less time near novel mice (F1,26 (interaction) = 17.16, p = 0.0003, two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test, Bonferroni post hoc analysis of GH S vs. j-SI S, p < 0.0001 GH: n = 12, j-SI: n = 16). S, social; O, object. c (Left) Bdnf expression measured using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) in microglia recovered from the cortex was higher in the j-SI mice than in the GH mice (t(22) = 4.876, p < 0.0001, unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test, GH: n = 12, j-SI: n = 12). (Right) Bdnf expression measured using RT-qPCR in microglia recovered from the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) was higher in j-SI than in GH mice (t(6) = 2.818, p = 0.0304, unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test, GH: n = 4 (from 16 mice), j-SI: n = 4 (from 16 mice)). The value was log-transformed with a base of 10 because of the right-skewed distribution. Each dot indicates the expression of Bdnf in microglia collected from the mPFC of four mice. d (Left) Schema of the GH and j-SI mice time series. The experiments started at P35. (right) Bdnf expression measured using RT-qPCR in microglia recovered from the cortex at P35 was higher in the j-SI mice than in the GH mice (t(14) = 4.353, p = 0.0007, unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test, GH: n = 8, j-SI: n = 8). *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. 2 M: two months of age, A.U.: arbitrary unit.