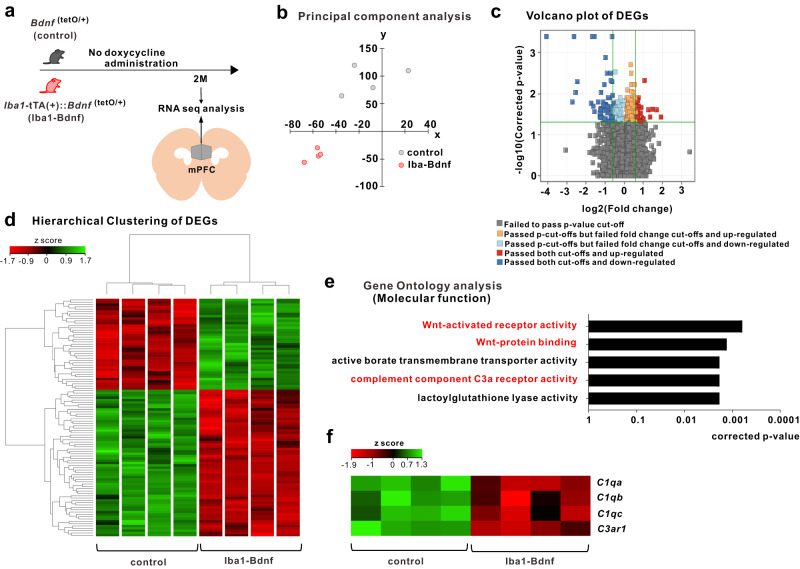
Fig. 4. MG-BDNF overexpression affects the complement system.
a RNA-seq analysis of the mPFC in adult Bdnf(tetO/+) (n = 4) and Iba1-tTA(+)::Bdnf(tetO/+) (n = 4) mice without doxycycline. The experiments were started at P64. b Principal component analysis revealing gene expression differences between the Bdnf(tetO/+) and Iba1-tTA(+)::Bdnf(tetO/+) mice. c Volcano plot of differentially expressed genes (DEGs). The thresholds are log2 fold change >1.5 and p < 0.05. d Heatmap and hierarchical clustering of DEGs between Bdnf(tetO/+) and Iba1-tTA(+)::Bdnf(tetO/+) mice. The thresholds are log2 fold change >1.5 and p < 0.05. Gene expression levels are indicated in the heatmap by the Z-scores in the legend. e The Gene Ontology analysis of down-regulated DEGs in the Iba1-tTA(+)::Bdnf(tetO/+) mice compared with Bdnf(tetO/+) mice suggested the involvement of the Wnt signaling pathway (Wnt-activated receptor pathway, p = 0.0006; Wnt-protein binding, p = 0.0013) and complement component C3a receptor activity (p = 0.0018) in molecular function. f Differences in expression levels of selected complement genes in Bdnf(tetO/+) and Iba1-tTA(+)::Bdnf(tetO/+) mice in RNA-Seq analysis. Gene expression levels are presented in the heatmap by the Z-scores in the legend. 2 M: two months of age, control: Bdnf(tetO/+) mice, Iba1-Bdnf: Iba1-tTA(+)::Bdnf(tetO/+) mice.