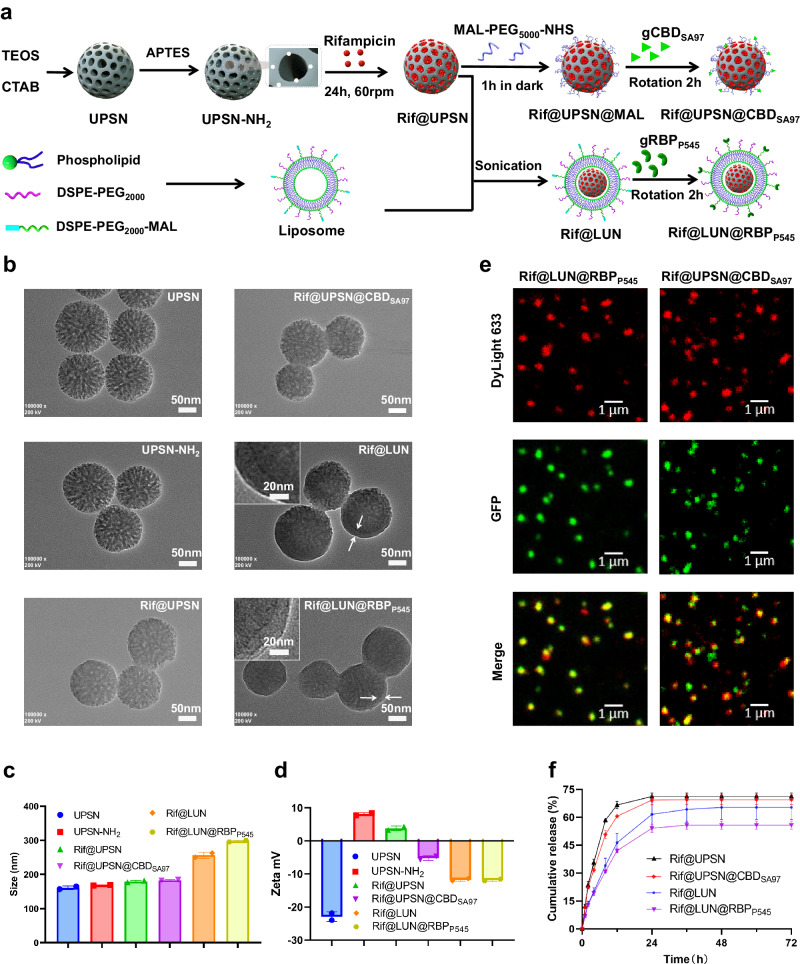
Fig. 3. Characterization of antibiotic-loaded nanodelivery systems.
a Preparation routes of Rif@LUN@RBPP545 and Rif@UPSN@CBDSA97. b Transmission electron microscope images of UPSN, UPSN-NH2, Rif@UPSN, Rif@UPSN@CBDSA97, Rif@LUN, and Rif@LUN@RBPP545. c Average hydrodynamic size of UPSN, UPSN-NH2, Rif@UPSN, Rif@UPSN@CBDSA97, Rif@LUN, and Rif@LUN@RBPP545 measured by dynamic light scattering. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 2 independent experiments). d Surface zeta-potential of UPSN, UPSN-NH2, Rif@UPSN, Rif@UPSN@CBDSA97, Rif@LUN, and Rif@LUN@RBPP545 in ultrapure water. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 2 independent experiments). e Confocal laser scanning microscopy images of Rif@LUN@RBPP545 and Rif@UPSN@CBDSA97 in which USPN was labeled with DyLight 633 (red) and the targeting devices were fused with GFP (green). f Release profiles of rifampicin payload from the nanoparticles in PBS at 37 °C. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3 independent experiments). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.