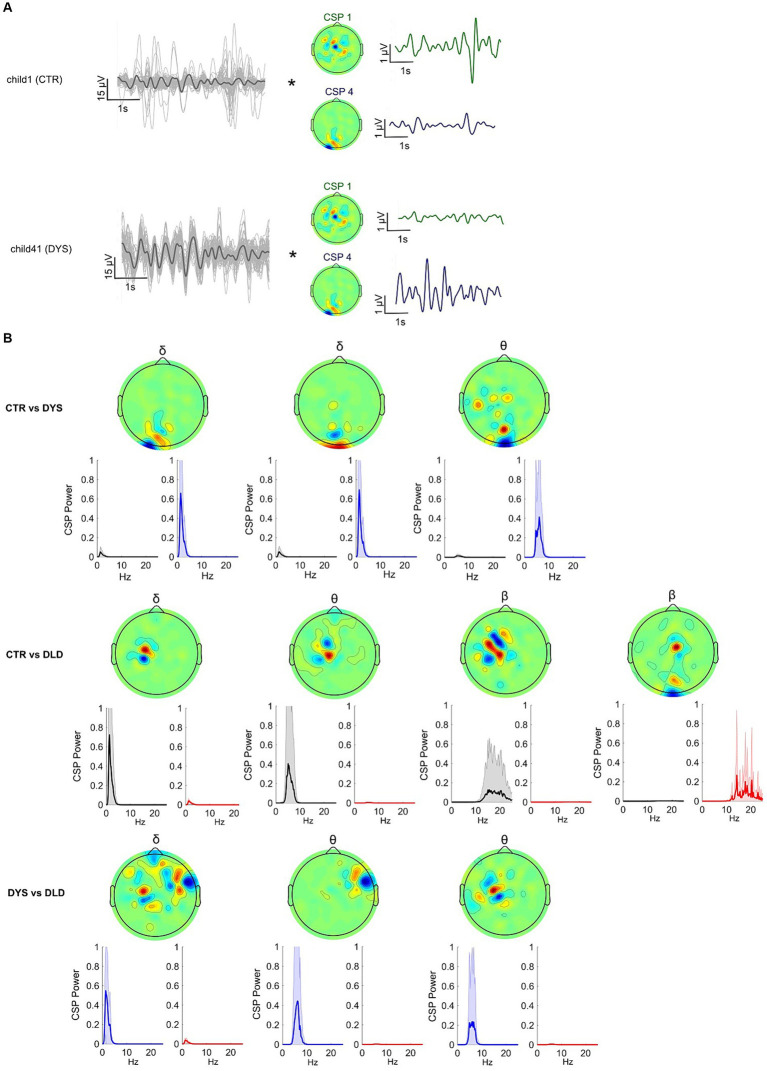
Figure 4.
Common Spatial Patterns (CSP) enable discrimination between dyslexic, DLD and typically-developing children during speech listening (story listening task). (A) Spatial filtering applied to the original EEG epochs (each channel depicted in grey, average in black). Spatial filters allow discrimination of EEG signals from experimental groups in the story listening task by selectively maximizing the signal variance for one group while minimizing for the other. (B) CSP filters for delta, theta and beta showing average power for each group for each filter. These CSPs showed significant differences at the group level (p < 0.05, Bonferroni corrected). Upper panel shows filters yielding significant group differences for the typically-developing children vs. dyslexic, middle panel for the typically-developing vs. DLD children and lower panel for the dyslexic vs. DLD children.