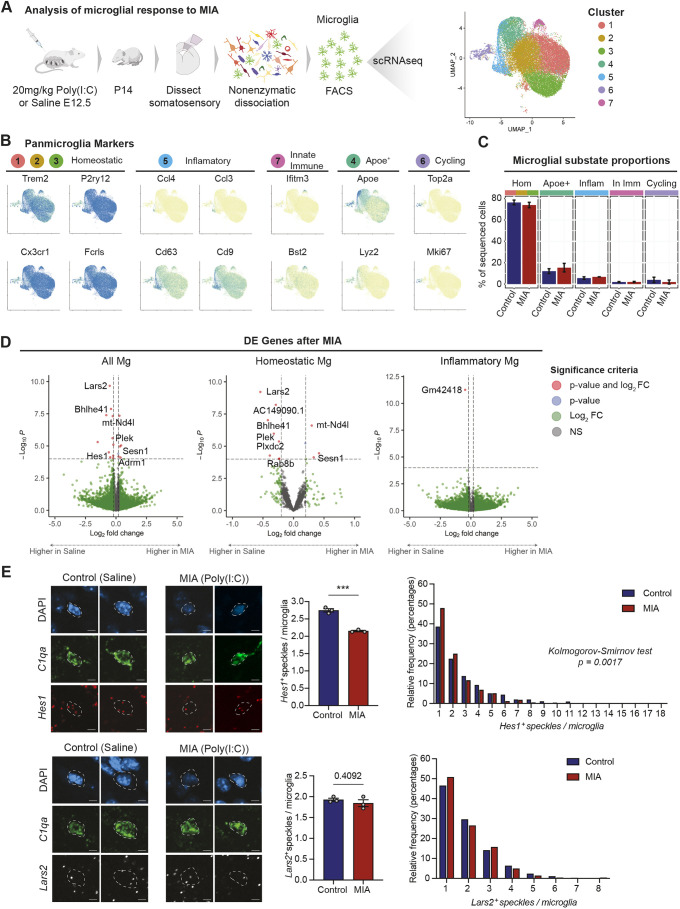
Fig. 4.
Persistent transcriptional changes in microglia after MIA. (A) Overview of experimental design and UMAP visualization of microglia scRNA-seq data from the somatosensory cortex of P14 mice after maternal injection of saline or Poly(I:C) at E12.5. In total, we sequenced 28,474 microglia from a total of six P14 mice, two of which were treated with Poly(I:C) and four of which were treated with saline. Cells are colored by cluster. (B) UMAP plots from A colored for expression of homeostatic, inflammatory, innate immune, Apoe+ and cycling substate-specific microglial marker genes. (C) Bar plot showing P14 microglial substate proportions after maternal injection of saline when compared with Poly(I:C). Generalized mixed effects binomial models showed no significant changes in substate proportions between treatment groups. Error bars represent one standard deviation in substate proportion. (D) Volcano plots showing differentially expressed genes in microglia from the P14 somatosensory cortex after maternal Poly(I:C) or saline injection. Genes are color coded according to enrichment (log2FC>0.15 and -log10Benjamini-Hochberg adj. P<0.05). Dotted lines represent enrichment cut-offs. Top signature genes are annotated. Log fold-change and P-values were generated with a generalized linear model with Benjamini-Hochberg correction using DESeq2. (E) In situ hybridization for Hes1 and Lars2 in P14 control (saline injected at E12.5) and MIA [Poly(I:C) injected at E12.5] coronal sections. C1qa was used as microglia marker. Quantification showing higher levels of Hes1 expression in saline compared with MIA (data are mean±s.e.m, from n=3 mice, between 697 and 458 microglia for each group; unpaired t-test: Hes1, P=0.0004; Lars2, P=0.4092). Scale bars: 5 µm. Frequency distribution showing percentage of cells for each speckle count (n=3 mice, between 697 and 458 microglia for each group; Kolmogorov–Smirnov test: Hes1, P=0.0017; Lars2, P=0.6019). Created with BioRender.com.