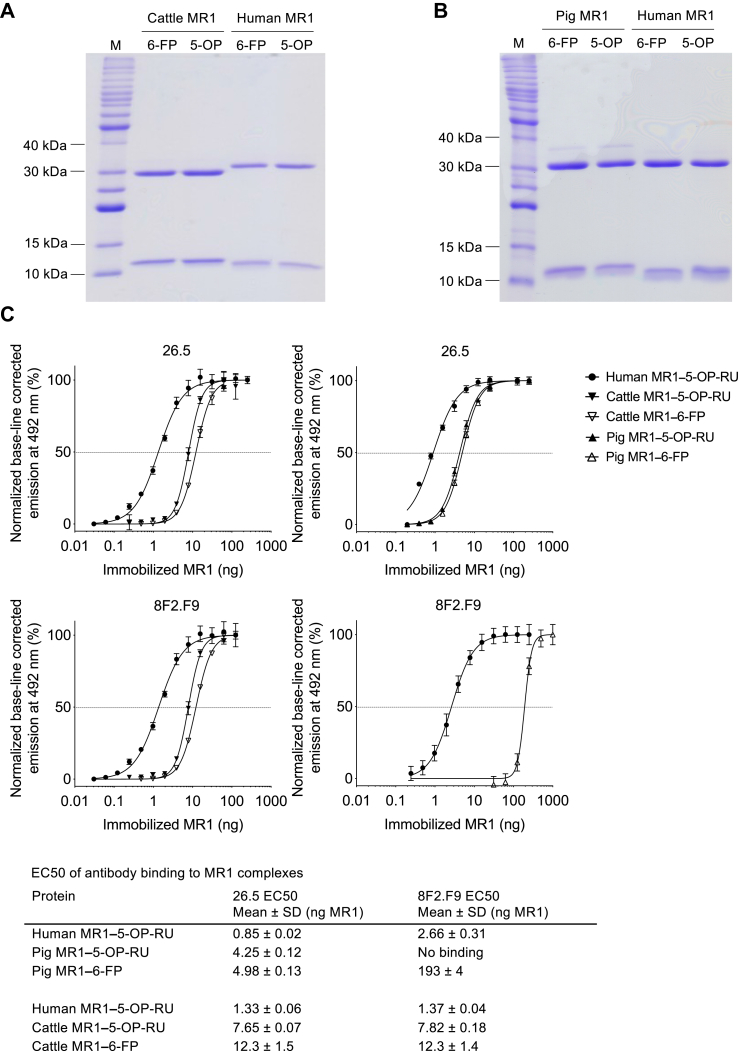
Figure 1.
Biochemical characterization of recombinant cattle and pig MR1–5-OP-RU and MR1–6-FP monomers.A and B, 15% SDS-PAGE under non-reducing conditions of 1.5 μg purified biotinylated cattle, pig, and human MR1 in complex with β2m and loaded with 5-OP-RU (5-OP) or 6-FP in comparison to a protein ladder (M) with molecular weights of proteins indicated as relevant. Accounting for loss of 4 H atoms and 2 H atoms due to the formation of two disulphide bonds in MR1 and one disulphide bond in β2m; the molecular weights of biotinylated MR1 and β2m are as follows: human: MR1: 32,258 Da, β2m: 11,860 Da; cattle MR1: 32403 Da, β2m: 11764 Da; pig MR1: 32526 Da, β2m: 11542 Da. C, 5-OP-RU- and 6-FP-loaded cattle and pig MR1 monomers in comparison to biotinylated human MR1–5-OP-RU (assessed previously alongside other species’ MR1 molecules, (64)) in ELISA with mAbs 26.5 and 8F2.F9 showing normalized, base-line corrected dose-response curves (n = 3, mean ± SD). EC50 values, as summarized in the table, were determined based on non-linear curve fits shown in the charts. 5-OP-RU, 5-(2-oxopropylideneamino)-6-d-ribitylaminouracil; 6-FP, 6-formylpterin; β2m, β2 microglobulin; MR1, MHC-I related protein 1.