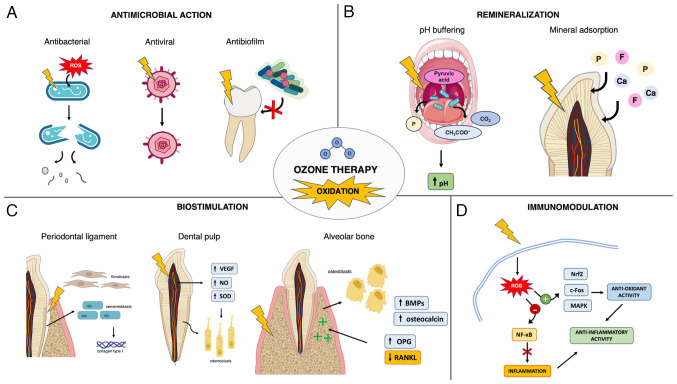
Figure 2.
Mechanisms involved in ozone interaction with dental tissues. (A) Antibacterial effect: Ozone causes damage to cytoplasmatic membrane and cell walls of bacteria and fungi, allowing ROS to enter cells and cause functional damage, cell lysis and death. Antiviral effect: Ozone induces conformational changes to viral structures such as the envelope and spike proteins, which leads to virus inactivation. Antibiofilm effect: Ozone induces alteration of salivary biomolecules and related binding sites, thus hampering biofilm formation and adhesion on dental surfaces. (B) Oxidation of the nucleic acids of microorganisms and of pyruvic acid in the oral cavity results in a pH buffering effect, facilitating a remineralizing environment. Oxidation causes microstructural surface changes, removal of surface organic components and proteins from enamel and dentine, which leads to enhanced deposition and diffusion of minerals within enamel and dentin, thus promoting remineralization and reduction of dentine hypersensitivity. (C) Effects on dental pulp: Mild oxidation promotes dental pulp homeostasis, vascularization and regeneration associated with increased expression of VEGF, NO and SOD, which leads to odontodifferentiation of dental pulp cells, odontoblast proliferation and the production of mineralized matrix. Effects on periodontal ligament: Ozone induces proliferation of periodontal cells and enhanced collagen type I synthesis, which results in periodontal tissue regeneration. Effects on alveolar bone: Ozone induces increased osteoblast proliferation and activity, increased expression of osteocalcin and BMPs, reduced RANKL levels and increased OPG levels, which results in the promotion of bone healing and formation. (D) Ozone byproducts and oxidation cause mild ROS signaling and mitochondrial stress, which lead to activation of antioxidant pathways and inhibition of pro-inflammatory pathways, resulting in an anti-inflammatory effects. Ozone also stimulates T-cell mediated immunity. Arrows indicate a causal effect, lightning bolts indicate ozone-induced oxidation and red crosses indicate prevention. ROS, reactive oxygen species; NO, nitrous oxide; SOD, superoxide dismutase; BMP, bone morphogenetic protein; RANKL, receptor activator of NF-κB ligand; OPG, osteoprotegerin; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor.