Figure 3.
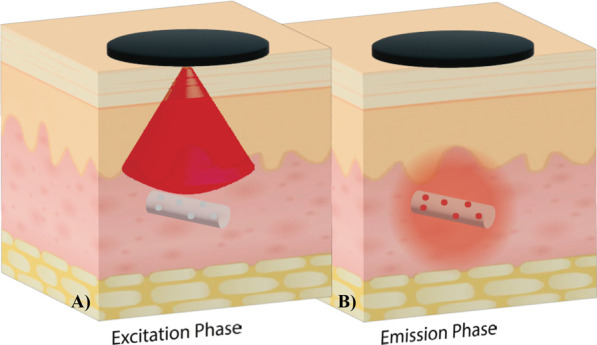
Collecting phosphorescence lifetime readings from an in vivo biosensor. In the excitation phase, the reader head emits red light to excite the biosensor’s phosphors, which begin to phosphoresce. In the emission phase, the reader head detects the infrared light emitted from the biosensor. The length of time before the phosphorescence is quenched is dependent on the oxygen interactions with the phosphors, allowing oxygen levels to be quantified. Phosphorescence lifetime measurements are unaffected by the implantation depth, which allows the optoelectronic components to remain outside the body, creating smaller and less invasive biosensors.
