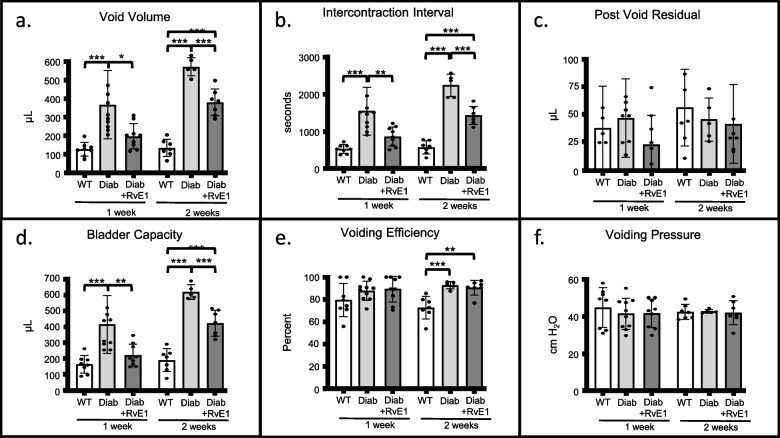
Fig. 5.
RvE1 improved signs of underactive bladder in diabetic mice. Male mice were separated into three experimental groups: wild-type mice (WT), diabetic mice treated with PBS (Diab), and diabetic mice treated daily with 25 μg/kg RvE1 (Diab + RvE1). Cystometry was performed after one or two weeks. Suprapubic tubes were placed in mice one week before cystometric analysis. During cystometry, mice were continuously infused with saline (15 μL/min) via the suprapubic tube. a Void volume. Void volume was measured by a scale situated underneath the mouse. b Intercontraction interval. Intercontraction interval was measured as the time between peaks in pressure that correspond with voids. c Post void residual volume. After the last void, post void residual volume was measured by attaching a 1 mL syringe to the suprapubic tube and drawing the plunger back halfway. Then the syringe was weighted on a tared scale. d Bladder capacity. Bladder capacity was calculated by adding void volume and post void residual. e Voiding efficiency. Voiding efficiency was calculated as void volume divided by bladder capacity. f Voiding Pressure. Voiding pressure was directly measured by an inline pressure transducer. For each parameter, the result of 5–10 micturition cycles was averaged for each mouse and considered n = 1. This average was then combined with the averages for each mouse and the results (the mean of the means) reported as mean ± SD. For the 1 week groups, WT n = 8 individual mice, Diab n = 10, and Diab + RvE1 n = 9. For the 2 weeks groups, WT n = 7, Diab n = 5, and Diab + RvE1 n = 7. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001